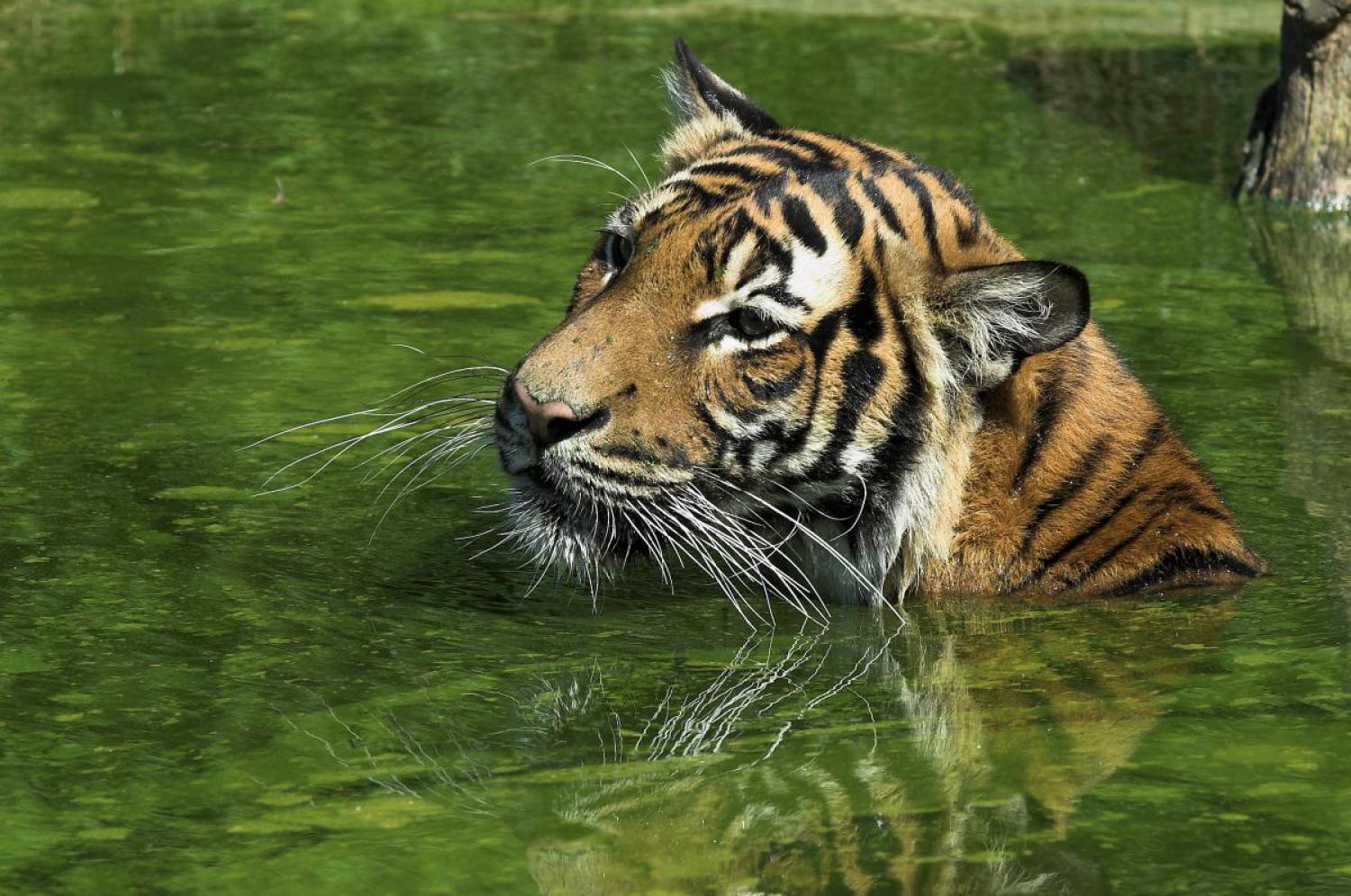
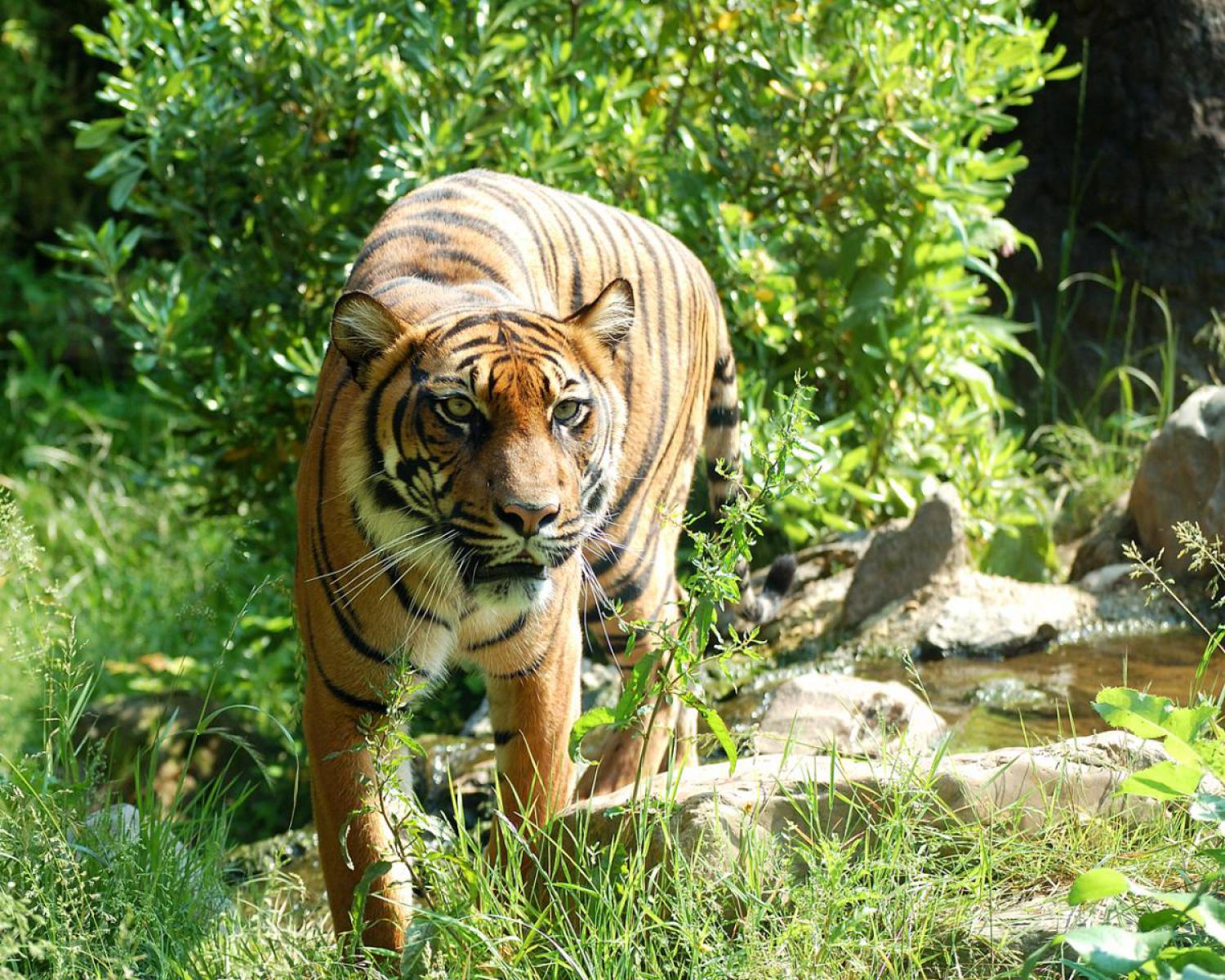
Species of Thailand
Tiger
Panthera tigris
Carolus Linnaeus, 1758
In Thai: เสือโคร่งอินโดจีน
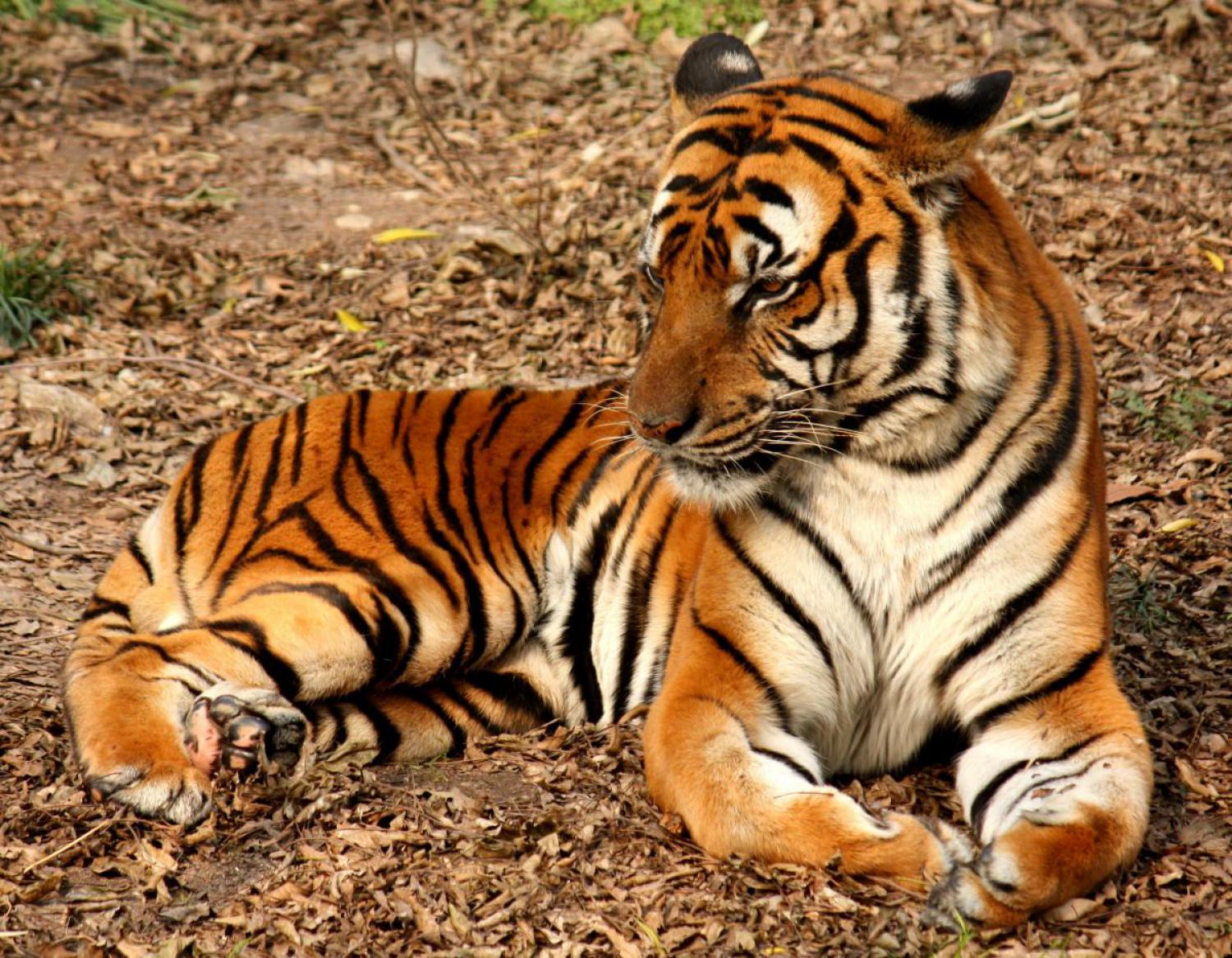
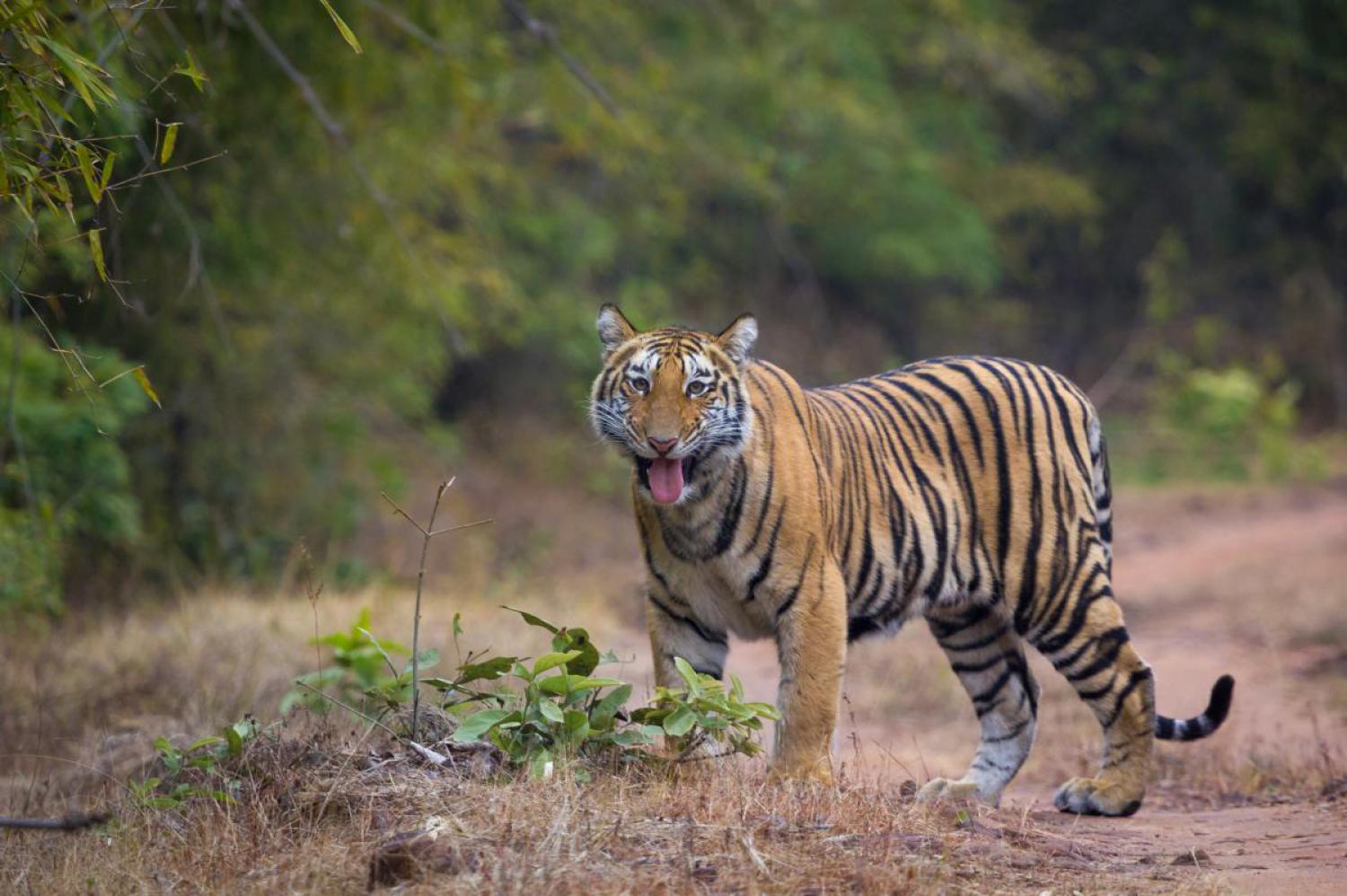
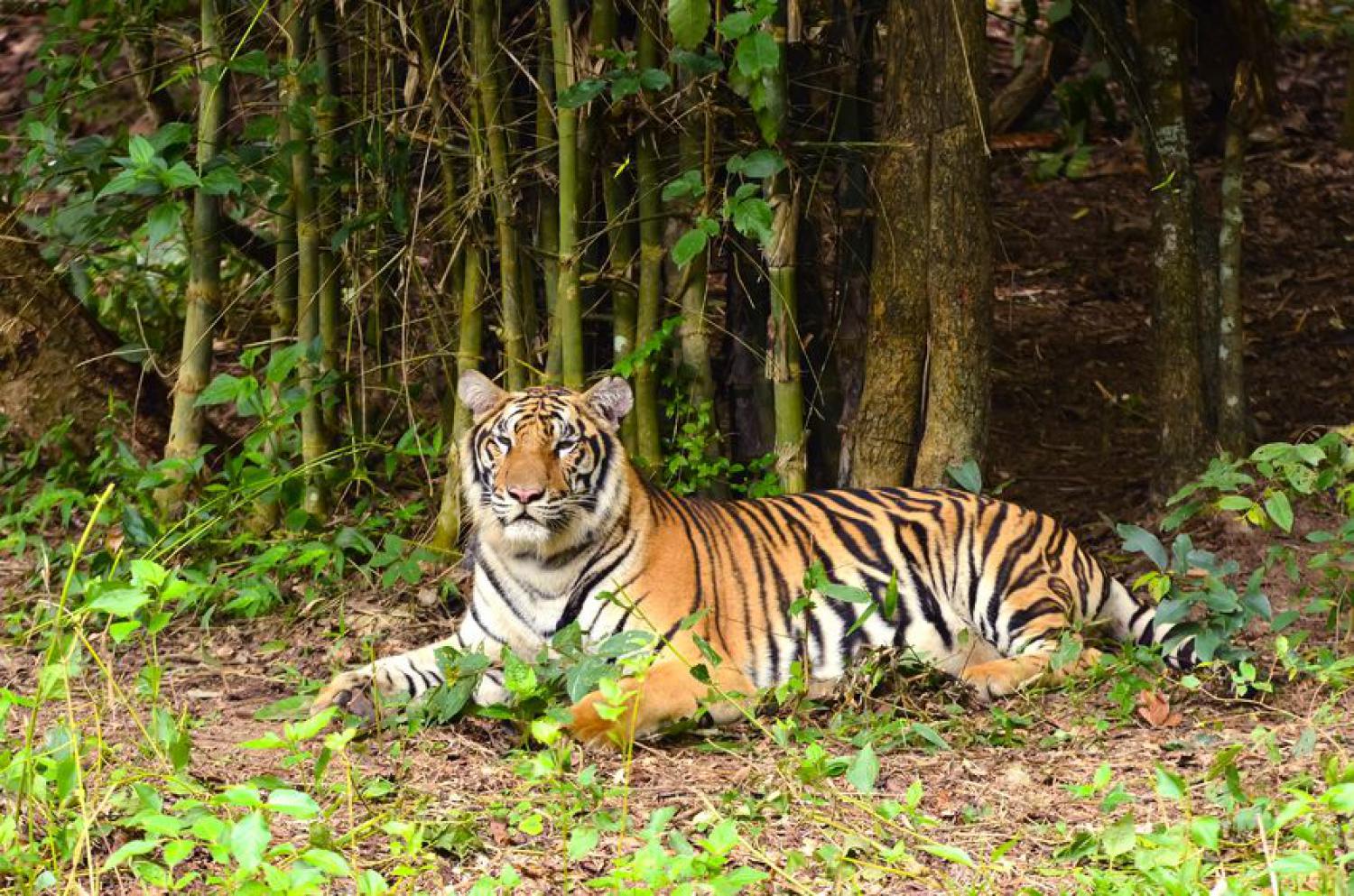
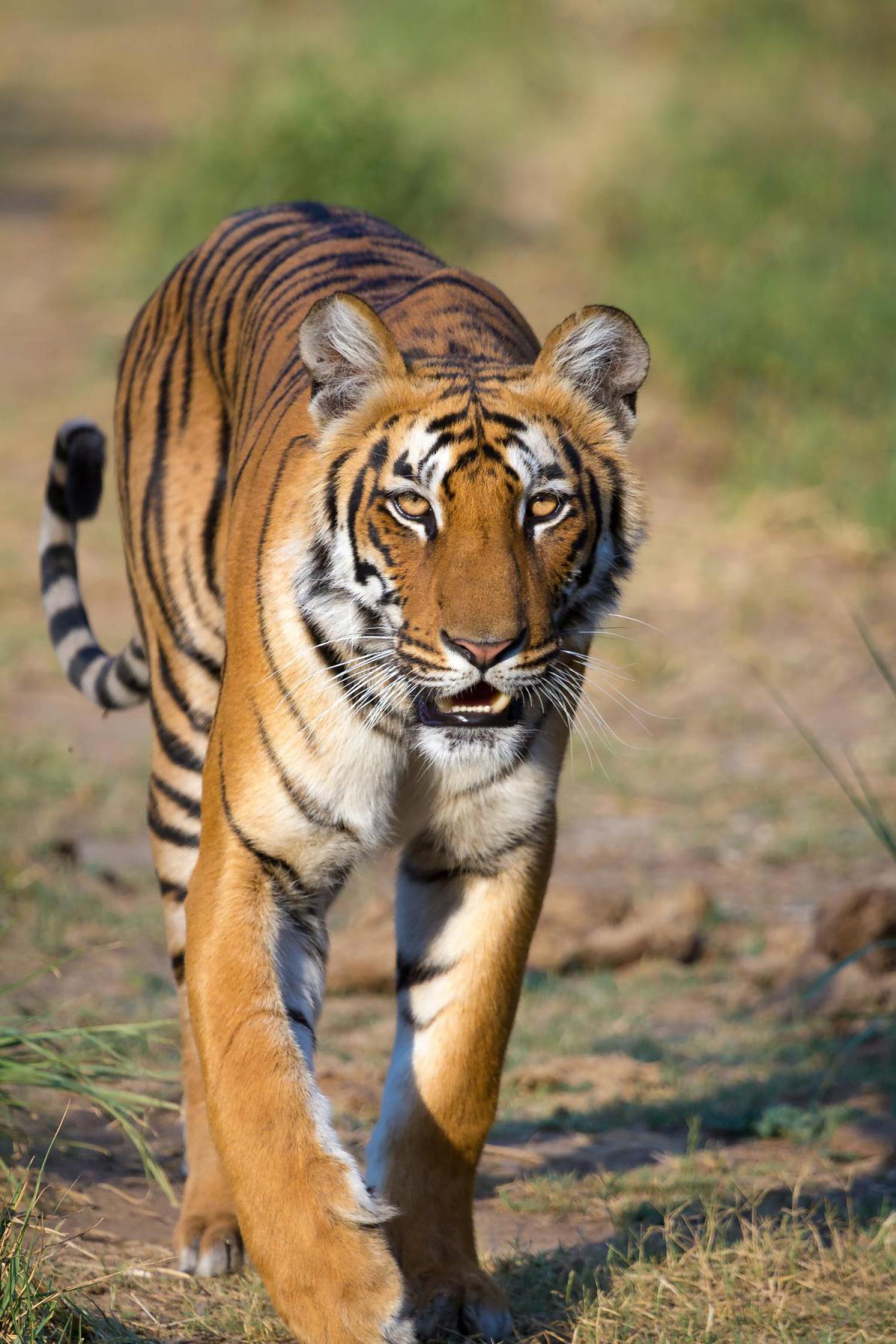
The tiger (Panthera tigris) is the largest cat species, reaching a total body length of up to 3.38 m over curves and exceptionally weighing up to 388.7 kg in the wild. Its most recognisable feature is a pattern of dark vertical stripes on reddish-orange fur with a lighter underside. The species is classified in the genus Panthera with the lion, leopard, jaguar and snow leopard. Tigers are apex predators, primarily preying on ungulates such as deer and bovids. They are territorial and generally solitary but social animals, often requiring large contiguous areas of habitat that support their prey requirements. This, coupled with the fact that they are indigenous to some of the more densely populated places on Earth, has caused significant conflicts with humans.
Tigers once ranged widely across Asia, from Turkey in the west to the eastern coast of Russia. Over the past 100 years, they have lost 93% of their historic range, and have been extirpated from southwest and central Asia, from the islands of Java and Bali, and from large areas of Southeast and Eastern Asia. Today, they range from the Siberian taiga to open grasslands and tropical mangrove swamps. The remaining six tiger subspecies have been classified as endangered by IUCN. The global population in the wild is estimated to number between 3, 062 and 3, 948 individuals, down from around 100, 000 at the start of the 20th century, with most remaining populations occurring in small pockets isolated from each other, of which about 2, 000 exist on the Indian subcontinent. Major reasons for population decline include habitat destruction, habitat fragmentation and poaching. The extent of area occupied by tigers is estimated at less than 1184911 km2, a 41% decline from the area estimated in the mid-1990s.
Tigers are among the most recognisable and popular of the world's charismatic megafauna. They have featured prominently in ancient mythology and folklore, and continue to be depicted in modern films and literature. They appear on many flags, coats of arms, and as mascots for sporting teams. The tiger is the national animal of Bangladesh, India, Vietnam, Malaysia and South Korea.
Taxonomy and etymology
In 1758, Linnaeus first described the species in his work Systema Naturae under the scientific name Felis tigris. In 1929, the British taxonomist Reginald Innes Pocock subordinated the species under the genus Panthera using the scientific name Panthera tigris.
The word Panthera is probably of Oriental origin and retraceable to the Ancient Greek word panther, the Latin word panthera, the Old French word pantere, most likely meaning "the yellowish animal", or from pandarah meaning whitish-yellow. The derivation from Greek pan- ("all") and ther ("beast") may be folk etymology.
The specific epithet, tigris, as well as the common name, tiger, come from the Middle English tigre and the Old English tigras (a plural word), both used for the animal. These derive from the Old French tigre, itself a derivative of the Latin word tigris and the Greek word tigris. The original source may have been the Persian tigra meaning pointed or sharp and the Avestan tigrhi meaning an arrow, perhaps referring to the speed with which a tiger launches itself at its prey.
Evolution
The tiger's closest living relatives were previously though to be the lion, leopard and jaguar, all of which are classified under the genus Panthera. A 2010 genetic analysis shows the tiger began evolving 3.2 million years ago, and it may be more closely related to the snow leopard than to the other Panthera species. The oldest remains of an extinct tiger relative, called Panthera zdanskyi or the Longdan tiger, have been found in the Gansu province of northwestern China. This species is considered to be a sister taxon to the extant tiger and lived about 2 million years ago, at the beginning of the Pleistocene. It was smaller than the modern tiger, being the size of a jaguar, and probably did not have the same coat pattern. Despite being considered more "primitive", the Longdan tiger was functionally and possibly ecologically similar to its modern cousin. As Panthera zdanskyi lived in northwestern China, that may have been where the tiger lineage originated. Tigers grew in size, possibly in response to adaptive radiations of prey species like deer and bovids which may have occurred in Southeast Asia during the early Pleistocene.
The earliest fossils of true tigers are from Java, and are between 1.6 and 1.8 million years old. Distinct fossils are known from the early and middle Pleistocene deposits in China and Sumatra. A subspecies called the Trinil tiger (Panthera tigris trinilensis) lived about 1.2 million years ago and is known from fossils found at Trinil in Java.
Tigers first reached India and northern Asia in the late Pleistocene, reaching eastern Beringia (but not the American Continent), Japan, and Sakhalin. Fossils found in Japan indicate the local tigers were, like the surviving island subspecies, smaller than the mainland forms, an example of insular dwarfism. Until the Holocene, tigers also lived in Borneo, as well as on the island of Palawan in the Philippines.
The tiger's full genome sequence was published in 2013. It and other cat genomes were found to have similar repeat composition and an appreciably conserved synteny.
Subspecies
There are 10 recognized tiger subspecies. One, the Trinil, became extinct in prehistoric times. The remaining subspecies all survived at least into the mid-20th century; three of these are also considered extinct. Their historical range in Bangladesh, Siberia, Iran, Afghanistan, India, China, and southeast Asia, including three Indonesian islands, is severely diminished today. The modern subspecies are:
| Subspecies | Description |
|---|---|
| Bengal tiger (P. t. tigris), also called the Indian tiger | Lives in India, Nepal, Bhutan, and Bangladesh, and is the most common subspecies. In 2011, the total adult population was estimated at 1, 520–1, 909 in India, 440 in Bangladesh, 155 in Nepal and 75 in Bhutan. In 2014, the population in India was estimated at 2, 226. It lives in alluvial grasslands, subtropical and tropical rainforests, scrub forests, wet and dry deciduous forests, and mangroves. It is the second-largest of the surviving subspecies. Males attain a total nose-to-tail length of 270 to 310 cm and weigh between 180 to 258 kg, while females range from 240 to 265 cm and 100 to 160 kg. In northern India and Nepal, the average is larger; males can weigh up to 235 kg, while females average 140 kg. Coat color varies from light yellow to reddish yellow with black stripes. |
| Indochinese tiger (P. t. corbetti), also called Corbett's tiger | Is found in Cambodia, China, Laos, Burma, Thailand, and Vietnam. In 2010 the total population was estimated at about 350 individuals. Their preferred habitat is forests in mountainous or hilly regions. Males average 108 cm in total length and weigh between 150 – 195 kg, while females average 96 cm and 100 – 130 kg. |
| Malayan tiger (P. t. jacksoni) | Exclusively found in the southern part of the Malay Peninsula. Was not considered a subspecies in its own right until a 2004 genetic analysis showed that they are distinct in mtDNA and micro-satellite sequences from the Indochinese subspecies. As of 2014 the total population is estimated at fewer than 500 individuals, though a new report from September that year estimated it at between 250 and 340 individuals. Males range in total length from 190 - 280 cm and weigh between 47.2 to 129.1 kg, while females range from 180 - 260 cm and 24 to 88 kg. |
| Siberian tiger (P. t. altaica), also known as the Amur tiger | Inhabits the Amur-Ussuri region of Primorsky Krai and Khabarovsk Krai in far eastern Siberia, with the exception of a small population in Hunchun National Siberian Tiger Nature Reserve in northeastern China, near the border of North Korea. In 2005, there were 331–393 adult and subadult Siberian tigers in the region, with a breeding adult population of about 250 individuals. As of 2015, there an estimated population of 480-540 individuals in the Russian Far East. It is the largest subspecies and ranks among the largest felids ever to have existed. Males have a head and body length of between 190 - 230 cm and weigh between 180 to 306 kg, while females average 160 - 180 cm and 100 to 167 kg. Tail length is about 60 - 110 cm. Compared to other subspecies, Siberian tigers have thicker coats, paler hues, and fewer stripes in dark brown instead of black. |
| South China tiger (P. t. amoyensis), also known as the Amoy or Xiamen tiger | Is the most critically endangered subspecies of tiger, and one of the 10 most endangered animals in the world. Despite unconfirmed reports and some evidence of footprints, there has been no confirmed wild sighting in over 25 years, leading experts to consider it "functionally extinct", with the entire known population of roughly 65+ individuals held in captivity. It is the second-smallest subspecies. Males range in total length from 230 - 260 cm and weigh between 130 to 180 kg, while females range from 220 - 240 cm and 100 to 110 kg. The South China tiger is considered to be the most ancient of the tiger subspecies and is distinguished by a particularly narrow skull, long nose, rhombus-like stripes and vivid orange colour. |
| Sumatran tiger (P. t. sumatrae) | Found only on the island of Sumatra, and is thus the last surviving of the three Indonesian island subspecies. Listed as a distinct subspecies as of 1998, when genetic testing revealed the presence of unique genetic markers, and is critically endangered. As of 2014 the wild population is estimated at between 400 and 500, seen chiefly in the island's national parks. It is the smallest of all living tigers. Males range in total length from 220 to 255 cm and weigh between 100 to 140 kg, while females range between 215 to 230 cm and 75 to 110 kg. Their reduced size is an adaptation to the thick, dense forests and smaller prey in their native habitat. This subspecies also has the darkest coat, with more narrowly spaced stripes and a longer mane and beard. |
| Subspecies | Description |
|---|---|
| Bali tiger (P. t. balica) | Was limited to the Indonesian island of Bali. Had a weight of 90 - 100 kg in males and 65 - 80 kg in females. Bali tigers were hunted to extinction; the last Bali tiger, an adult female, is thought to have been killed at Sumbar Kima, West Bali, on 27 September 1937, though there were unconfirmed reports that villagers found a tiger corpse in 1963. The Bali tiger is reported to have had some spots in between its stripes. |
| Caspian tiger (P. t. virgata), also known as the Hyrcanian tiger or Turan tiger | Was found in the sparse forest habitats and riverine corridors west and south of the Caspian Sea and east through Central Asia into the Takla-Makan desert of Xinjiang, and had been recorded in the wild until the early 1970s. The Amur tiger is the genetically closest living relative of the Caspian tiger. |
| Javan tiger (P. t. sondaica) | Was limited to the island of Java, and had been recorded until the mid-1970s. Javan tigers were larger than Bali tigers; males weighed 100 - 141 kg and females 75 - 115 kg. After 1979, no more sightings were confirmed in the region of Mount Betiri. An expedition to Mount Halimun Salak National Park in 1990 did not yield any definite, direct evidence for the continued existence of tigers. |
An analysis of craniodental and pelage morphology, ecology, and molecular biology of the tiger subspecies indicates that they have many traits in common and that the genetic diversity between them is low. The authors of this analysis suggest to group the Bengal, Indochinese, Malayan, South China, and Siberian tiger subspecies to the Continental tiger Panthera tigris tigris; and the Sumatran, Javan and Bali tiger subspecies to the Sunda tiger Panthera tigris sondaica. This classification is intended to facilitate tiger conservation management, both regarding breeding programmes in zoos and future translocations in the wild. The classification is criticized by several geneticists, who maintain that the currently recognized nine subspecies can be distinguished genetically.
Hybrids
Lions have been known to breed with tigers (most often the Amur and Bengal subspecies) to create hybrids called ligers and tigons. Such hybrids were once commonly bred in zoos, but this is now discouraged due to the emphasis on conservation. Hybrids are still bred in private menageries and in zoos in China.
The liger is a cross between a male lion and a tigress. Because the lion sire passes on a growth-promoting gene, but the corresponding growth-inhibiting gene from the female tiger is absent, ligers grow far larger than either parent. They share physical and behavioural qualities of both parent species (spots and stripes on a sandy background). Male ligers are sterile, but female ligers are often fertile. Males have about a 50% chance of having a mane, but, even if they do, their manes will be only around half the size of that of a pure lion. Ligers are typically between 10 and 12 feet in length, and can weigh between 800 and 1, 000 pounds or more.
The less common tigon is a cross between a lioness and a male tiger. Because the male tiger does not pass on a growth-promoting gene and the lioness passes on a growth inhibiting gene, tigons are often relatively small, only weighing up to 150 kg (350 lb), which is about 10–20% smaller than lions. Like ligers, they have physical and behavioural traits from both parental species, and males are sterile. Females are sometimes fertile and have occasionally given birth to litigons when mated to a lion.
Description
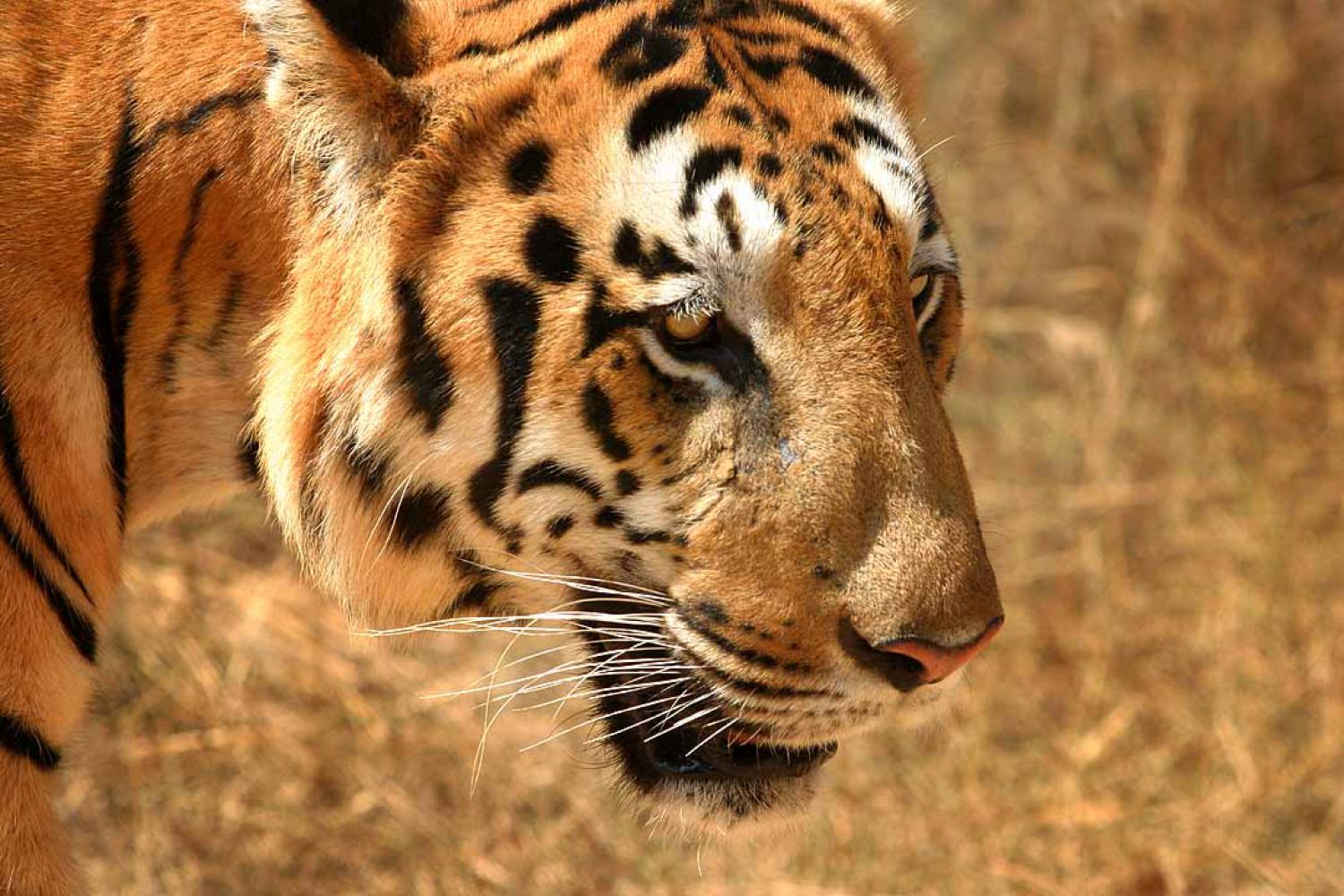
Tigers have muscular bodies with powerful forelimbs, large heads and long tails. The pelage is dense and heavy; coloration varies between shades of orange and brown with white ventral areas and distinctive vertical black stripes, whose patterns are unique to each individual. Their function is likely for camouflage in vegetation such as long grass with strong vertical patterns of light and shade. The tiger is one of only a few striped cat species; it is not known why spots are the more common camouflage pattern among felids. The tiger's stripes are also found on the skin, so that if it were to be shaved, its distinctive coat pattern would still be visible. They have a mane-like heavy growth of fur around the neck and jaws and long whiskers, especially in males. The pupils are circular with yellow irises. The small, rounded ears have a prominent white spot on the back, surrounded by black. These false "eyespots", called ocelli, apparently play an important role in intraspecies communication.
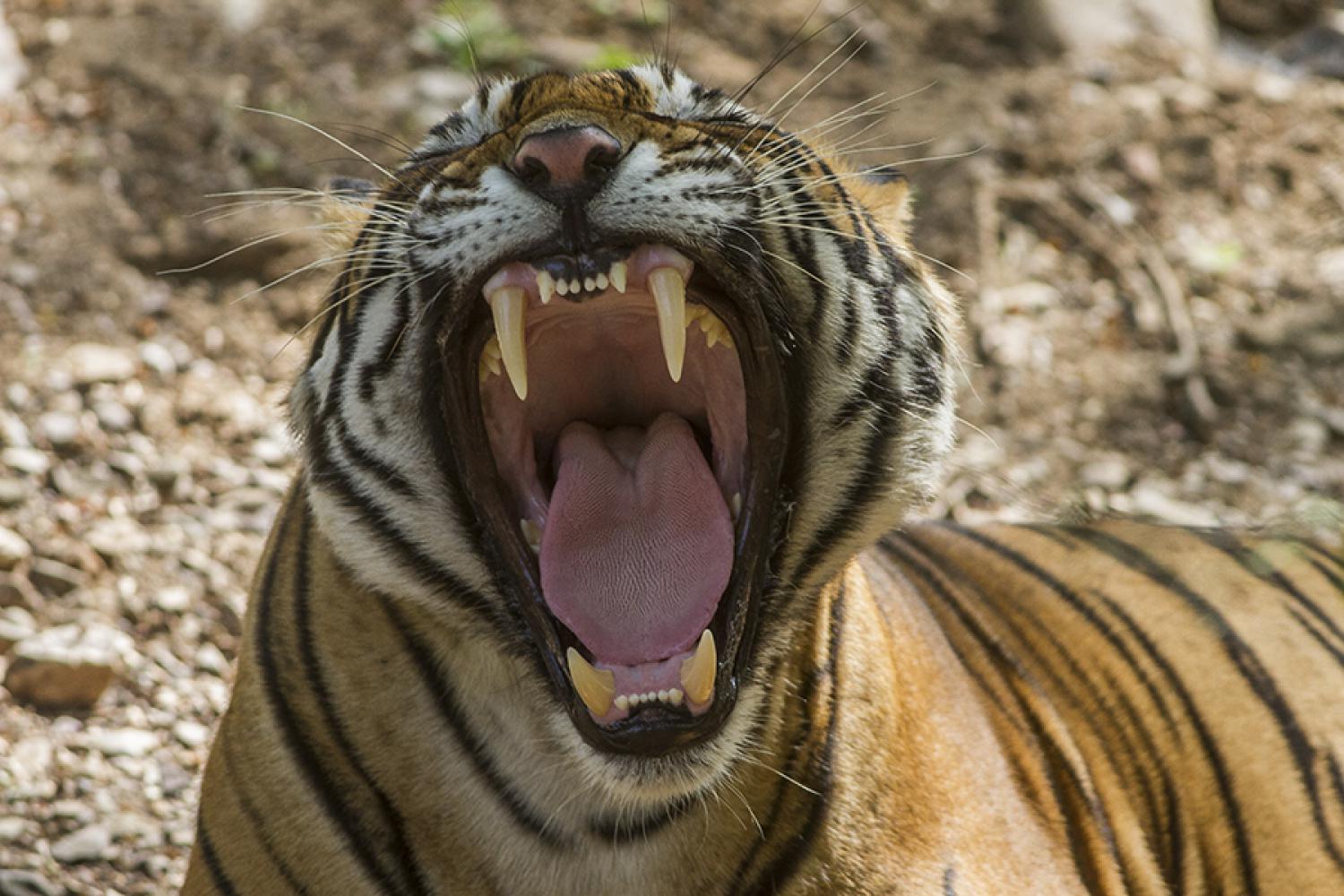
The skull is similar to that of the lion, though the frontal region is usually not as depressed or flattened, with a slightly longer postorbital region. The skull of a lion has broader nasal openings. However, due to variation in skulls of the two species, the structure of the lower jaw is a more reliable indicator of species. The tiger also has fairly stout teeth; the somewhat curved canines are the longest among living felids with a crown height of up to 90 mm.
The oldest recorded captive tiger lived for 26 years. A wild specimen, having no natural predators, could in theory live to a comparable age.
Size
Tigers are the most variable in size of all big cats, much more so than lions. The Bengal and Siberian subspecies are the tallest at the shoulder and thus considered the largest living felids, ranking with the extinct Caspian tiger among the biggest that ever existed. An average adult male tiger from Northern India or Siberia outweighs an average adult male lion by around 45.5 kg. Males vary in total length from 250 to 390 cm and weigh between 90 to 306 kg with skull length ranging from 316 to 383 mm. Females vary in total length from 200 to 275 cm, weigh 65 to 167 kg with skull length ranging from 268 to 318 mm. In either sex, the tail represents about 0.6 to 1.1 m of total length.
Body size of different populations seems to be correlated with climate—Bergmann's rule—and can be explained by thermoregulation. Large male Siberian tigers can reach a total length of more than 3.5 m over curves and 3.3 m between pegs, and can weigh up to 306 kg. This is considerably larger than the weight of 75 to 140 kg reached by the smallest living subspecies, the Sumatran tiger. At the shoulder, tigers may variously stand 0.7 to 1.22 m tall. The current record weight in the wild was 389 kg for a Bengal tiger shot in 1967.
They are a notably sexually dimorphic species, females being consistently smaller than males. The size difference between males and females is proportionally greater in the larger tiger subspecies, with males weighing up to 1.7 times more than females. Males also have wider forepaw pads than females, enabling gender to be told from tracks.
Color variations
A well-known allele found only in the Bengal subspecies produces the white tiger, a color variant first recorded in the early 19th century and found in an estimated one in 10, 000 natural births. Genetically, whiteness is recessive: a cub is white only when both parents carry the allele for whiteness. It is not albinism, pigment being evident in the white tiger's stripes and in their blue eyes. The causative mutation changes a single amino acid in the transporter protein SLC45A2.
White tigers are more frequently bred in captivity, where the comparatively small gene pool can lead to inbreeding. This has given white tigers a greater likelihood of being born with physical defects, such as cleft palate, scoliosis (curvature of the spine), and strabismus (squint). Even apparently healthy white tigers generally do not live as long as their orange counterparts. Attempts have been made to cross white and orange tigers to remedy this, often mixing with other subspecies in the process.
Another recessive gene creates the "golden" or "golden tabby" color variation, sometimes known as "strawberry". Golden tigers have thicker than usual light-gold fur, pale legs, and faint orange stripes. Few golden tigers are kept in captivity; they are invariably at least part Bengal. Some golden tigers carry the white tiger gene, and when two such tigers are mated, they can produce some stripeless white offspring. Although a "pseudo-melanistic" effect—wide stripes that partially obscure the orange background—has been seen in some pelts, no true black tigers have been authenticated, with the possible exception of one dead specimen examined in Chittagong in 1846. These wholly or partially melanistic tigers, if they exist, are assumed to be intermittent mutations rather than a distinct species. There are further unconfirmed reports of a "blue" or slate-colored variant, the Maltese tiger. However, while some felids do exhibit this coloration as a solid coat, there is no known genetic configuration that would result in black stripes on a blue-gray background.
Distribution and habitat
In the past, tigers were found throughout Asia, from the Caucasus and the Caspian Sea to Siberia and the Indonesian islands of Java, Bali and Sumatra. Fossil remains indicate tigers were also present in Borneo and Palawan in the Philippines during the late Pleistocene and Holocene.
During the 20th century, tigers became extinct in western Asia and were restricted to isolated pockets in the remaining parts of their range. They were extirpated on the island of Bali in the 1940s, around the Caspian Sea in the 1970s, and on Java in the 1980s. This was the result of habitat loss and the ongoing killing of tigers and tiger prey. Today, their fragmented and partly degraded range extends from India in the west to China and Southeast Asia. The northern limit of their range is close to the Amur River in southeastern Siberia. The only large island they still inhabit is Sumatra. Since the beginning of the 20th century, tigers' historical range has shrunk by 93%. In the decade from 1997 to 2007, the estimated area known to be occupied by tigers has declined by 41%.
Tigers can occupy a wide range of habitat types, but will usually require sufficient cover, proximity to water, and an abundance of prey. Compared to the lion, the tiger prefers denser vegetation, for which its camouflage colouring is ideally suited, and where a single predator is not at a disadvantage compared with the multiple felines in a pride. A further habitat requirement is the placement of suitably secluded den locations, which may consist of caves, large hollow trees, or dense vegetation. Bengal tigers in particular live in many types of forests, including wet, evergreen, and the semievergreen of Assam and eastern Bengal; the swampy mangrove forest of the Ganges Delta; the deciduous forest of Nepal, and the thorn forests of the Western Ghats. In various parts of their range they inhabit or have inhabited additionally partially open grassland and savanna as well as taiga forests and rocky habitats.
Social activity
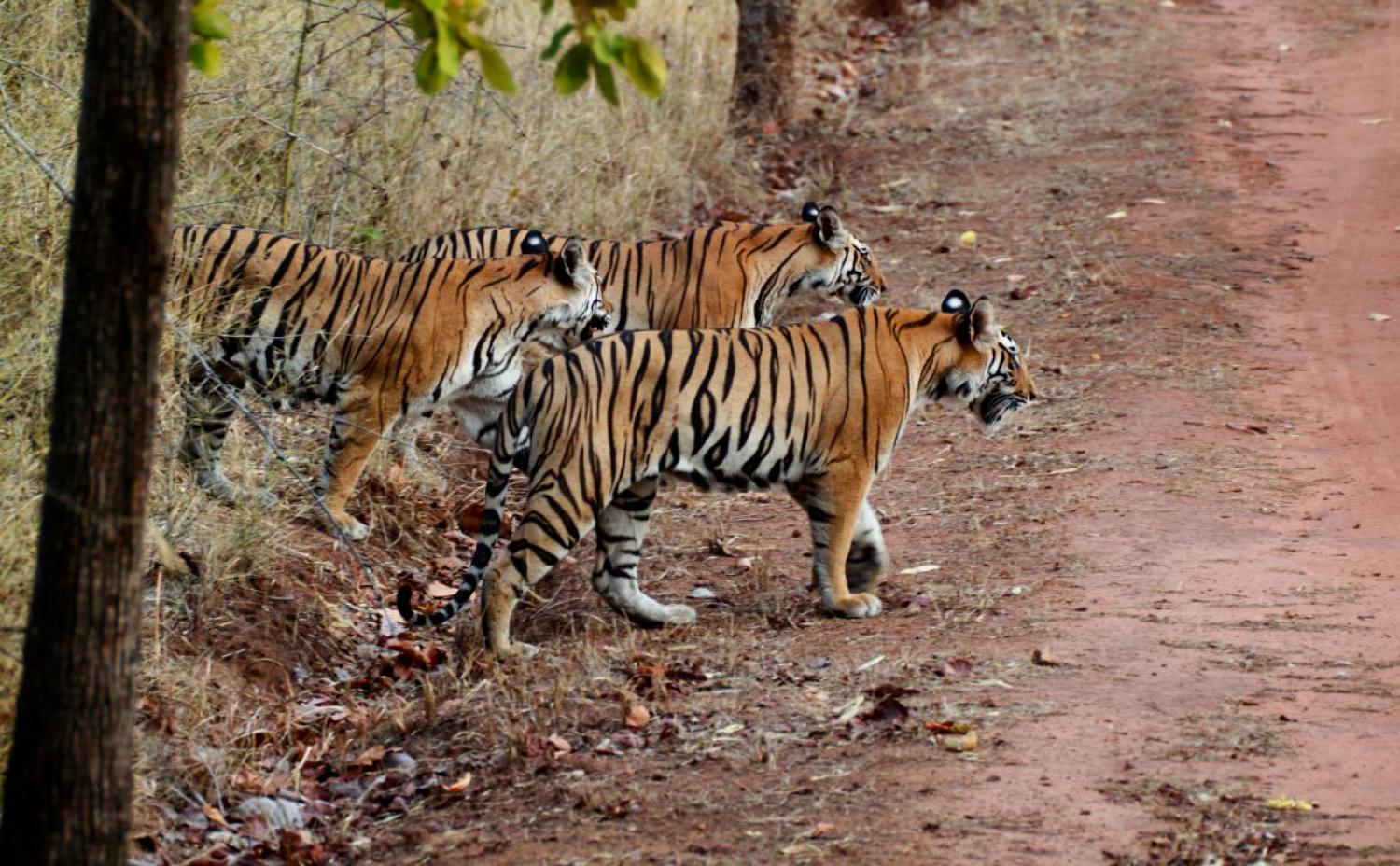
Adult tigers lead largely solitary lives. They establish and maintain territories but have much wider home ranges within which they roam. Resident adults of either sex generally confine their movements to their home ranges, within which they satisfy their needs and those of their growing cubs. Individuals sharing the same area are aware of each other's movements and activities. The size of the home range mainly depends on prey abundance, and, in the case of males, on access to females. A tigress may have a territory of 20 km2, while the territories of males are much larger, covering 60 to 100 km2. The range of a male tends to overlap those of several females, providing him with a large field of prospective mating partners.
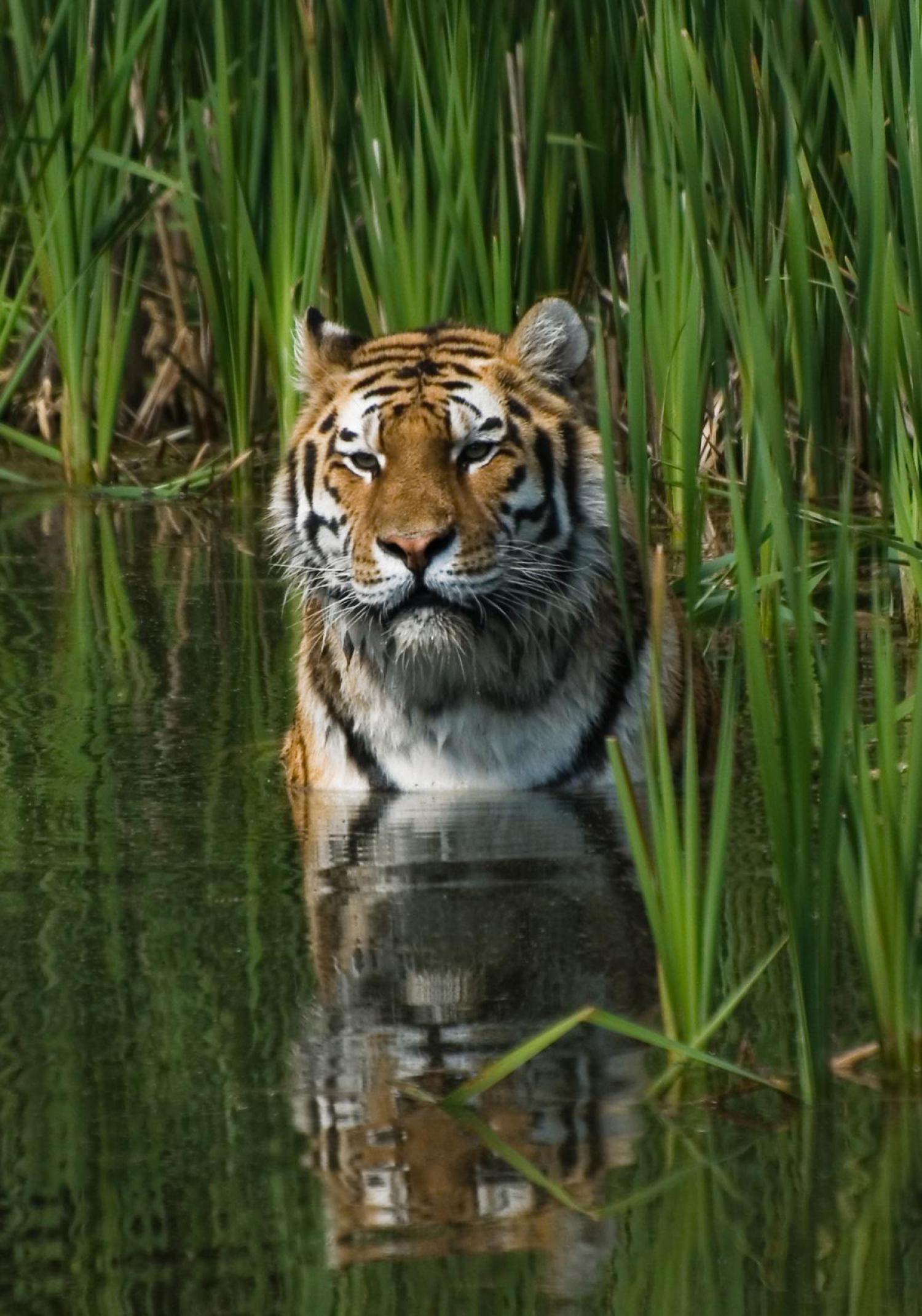
Unlike many felids, tigers are strong swimmers and often deliberately bathe in ponds, lakes and rivers as a means of keeping cool in the heat of the day. Among the big cats, only the jaguar shares a similar fondness for water. They may cross rivers up to 7 km across and can swim up to 29 km in a day. They are able to carry prey through or capture it in the water.
Young female tigers establish their first territories close to their mother's. The overlap between the female and her mother's territory reduces with time. Males, however, migrate further than their female counterparts and set out at a younger age to mark out their own area. A young male acquires territory either by seeking out an area devoid of other male tigers, or by living as a transient in another male's territory until he is older and strong enough to challenge the resident male. Young males seeking to establish themselves thereby comprise the highest mortality rate (30–35% per year) amongst adult tigers.
To identify his territory, the male marks trees by spraying urine and anal gland secretions, as well as marking trails with scat and marking trees or the ground with their claws. Females also use these "scrapes", as well as urine and scat markings. Scent markings of this type allow an individual to pick up information on another's identity, sex and reproductive status. Females in oestrus will signal their availability by scent marking more frequently and increasing their vocalizations.
Although for the most part avoiding each other, tigers are not always territorial and relationships between individuals can be complex. An adult of either sex will sometimes share its kill with others, even those who may not be related to them. George Schaller observed a male share a kill with two females and four cubs. Unlike male lions, male tigers allow females and cubs to feed on the kill before the male is finished with it; all involved generally seem to behave amicably, in contrast to the competitive behaviour shown by a lion pride. This quotation is from Stephen Mills' book Tiger, describing an event witnessed by Valmik Thapar and Fateh Singh Rathore in Ranthambhore National Park:
A dominant tigress they called Padmini killed a 250 kg male nilgai – a very large antelope. They found her at the kill just after dawn with her three 14-month-old cubs and they watched uninterrupted for the next ten hours. During this period the family was joined by two adult females and one adult male, all offspring from Padmini's previous litters, and by two unrelated tigers, one female the other unidentified. By three o'clock there were no fewer than nine tigers round the kill.
Male tigers are generally more intolerant of other males within their territories than females are of other females. Territory disputes are usually solved by displays of intimidation rather than outright aggression. Several such incidents have been observed in which the subordinate tiger yielded defeat by rolling onto its back and showing its belly in a submissive posture. Once dominance has been established, a male may tolerate a subordinate within his range, as long as they do not live in too close quarters. The most aggressive disputes tend to occur between two males when a female is in oestrus, and may rarely result in the death of one of the males.
Facial expressions include the "defense threat", where an individual bares its teeth, flattens its ears and its pupils enlarge. Both males and females show a flehmen response, a characteristic grimace, when sniffing urine markings but flehmen is more often associated with males detecting the markings made by tigresses in oestrus. Like other Panthera, tigers roar, particularly in aggressive situations, during the mating season or when making a kill. There are two different roars: the "true" roar is made using the hyoid apparatus and forced through an open mouth as it progressively closes, and the shorter, harsher "coughing" roar is made with the mouth open and teeth exposed. The "true" roar can be heard at up to 3 km away and is sometimes emitted three or four times in succession. When tense, tigers will moan, a sound similar to a roar but more subdued and made when the mouth is partially or completely closed. Moaning can be heard 400 m away. Chuffing, soft, low-frequency snorting similar to purring in smaller cats, is heard in more friendly situations. Other vocal communications include grunts, woofs, snarls, miaows, hisses and growls.
Tigers have been studied in the wild using a variety of techniques. The populations of tigers have been estimated using plaster casts of their pugmarks, although this method was criticized as being inaccurate. More recent attempts have been made using camera trapping and studies on DNA from their scat, while radio collaring has been used to track tigers in the wild.
Hunting and diet
In the wild, tigers mostly feed on large and medium-sized animals, preferring native ungulates weighing at least 90 kg. They typically have little or no deleterious effect on their prey populations. Sambar deer, chital, barasingha, wild boar, gaur, nilgai and both water buffalo and domestic buffalo, in descending order of preference, are the tiger's favoured prey in Tamil Nadu, India, while gaur and sambar are the preferred prey and constitute the main diet of tigers in other parts of India. They also prey on other predators, including dogs, leopards, pythons, sloth bears, and crocodiles. In Siberia, the main prey species are Manchurian wapiti and wild boar (the two species comprising nearly 80% of the prey selected) followed by sika deer, moose, roe deer, and musk deer. Asiatic black bears and Ussuri brown bears may also fall prey to tigers, and they constitute up to 40.7% of the diet of Siberian tigers depending on local conditions and the bear populations. In Sumatra, prey include sambar deer, muntjac, wild boar, Malayan tapir and orangutan. In the former Caspian tiger's range, prey included saiga antelope, camels, Caucasian wisent, yak, and wild horses. Like many predators, tigers are opportunistic and may eat much smaller prey, such as monkeys, peafowl and other ground-based birds, hares, porcupines, and fish.
Tigers generally do not prey on fully grown adult Asian elephants and Indian rhinoceros but incidents have been reported. More often, it is the more vulnerable small calves that are taken. Tigers have been reported attacking and killing elephants ridden by humans during tiger hunts in the nineteenth century. When in close proximity to humans, tigers will also sometimes prey on such domestic livestock as cattle, horses, and donkeys. Old or wounded tigers, unable to catch wild prey, can become man-eaters; this pattern has recurred frequently across India. An exception is in the Sundarbans, where healthy tigers prey upon fishermen and villagers in search of forest produce, humans thereby forming a minor part of the tiger's diet. Although almost exclusively carnivorous, tigers will occasionally eat vegetation for dietary fibre. The fruit of the slow match tree is a favorite.
Tigers are thought to be mainly nocturnal predators, but in areas where humans are typically absent, they have been observed via remote-controlled, hidden cameras, hunting in daylight. They generally hunt alone and ambush their prey as most other cats do, overpowering them from any angle, using their body size and strength to knock the prey off balance. Successful hunts usually require the tiger to almost simultaneously leap onto its quarry, knock it over, and grab the throat or nape with its teeth. Despite their large size, tigers can reach speeds of about 49 - 65 km/h but only in short bursts; consequently, tigers must be close to their prey before they break cover. If the prey catches wind of the tiger's presence before this, the tiger usually abandons the hunt rather than chase prey or battle it head-on. Horizontal leaps of up to 10 m have been reported, although leaps of around half this distance are more typical. One in 2 to 20 hunts, including stalking near potential prey, ends in a successful kill.
When hunting larger animals, tigers prefer to bite the throat and use their powerful forelimbs to hold onto the prey, often simultaneously wrestling it to the ground. The tiger remains latched onto the neck until its target dies of strangulation. By this method, gaurs and water buffaloes weighing over a ton have been killed by tigers weighing about a sixth as much. Although they can kill healthy adults, tigers often select the calves or infirm of very large species. Healthy adult prey of this type can be dangerous to tackle, as long, strong horns, legs and tusks are all potentially fatal to the tiger. No other extant land predator routinely takes on prey this large on their own. Whilst hunting sambars, which comprise up to 60% of their prey in India, tigers have reportedly made a passable impersonation of the male sambar's rutting call to attract them. With smaller prey, such as monkeys and hares, the tiger bites the nape, often breaking the spinal cord, piercing the windpipe, or severing the jugular vein or common carotid artery. Though rarely observed, some tigers have been recorded to kill prey by swiping with their paws, which are powerful enough to smash the skulls of domestic cattle, and break the backs of sloth bears.
During the 1980s, a tiger named "Genghis" in Ranthambhore National Park was observed frequently hunting prey through deep lake water, a pattern of behaviour that had not previously been witnessed in over 200 years of observations. Moreover, he appeared to be unusually successful, with 20% of hunts ending in a kill.
After killing their prey, tigers sometimes drag it to conceal it in vegetative cover, usually pulling it by grasping with their mouths at the site of the killing bite. This, too, can require great physical strength. In one case, after it had killed an adult gaur, a tiger was observed to drag the massive carcass over a distance of 12 m. When 13 men simultaneously tried to drag the same carcass later, they were unable to move it. An adult tiger can go for up to two weeks without eating, then gorge on 34 kg of flesh at one time. In captivity, adult tigers are fed 3 to 6 kg of meat a day.
Interaction with other predators
Tigers usually prefer to eat prey they have caught themselves, but are not above eating carrion in times of scarcity and may even pirate prey from other large carnivores. Although predators typically avoid one another, if a prey item is under dispute or a serious competitor is encountered, displays of aggression are common. If these are not sufficient, the conflicts may turn violent; tigers may kill competitors as leopards, dholes, striped hyenas, wolves, bears, pythons and crocodiles on occasion. Tigers may also prey on these competitors. Attacks on smaller predators, such as badgers, lynxes, and foxes, are almost certainly predatory. Crocodiles, bears and large packs of dholes may win conflicts against tigers and in some cases even kill them.
The considerably smaller leopard avoids competition from tigers by hunting at different times of the day and hunting different prey. In India's Nagarhole National Park, most prey selected by leopards were from 30 to 175 kg against a preference for prey weighing over 176 kg in the tigers. The average prey weight in the two respective big cats in India was 37.6 kg against 91.5 kg. With relatively abundant prey, tigers and leopards were seen to successfully coexist without competitive exclusion or interspecies dominance hierarchies that may be more common to the African savanna (where the leopard may coexist with the lion). Lone golden jackals expelled from their pack have been known to form commensal relationships with tigers. These solitary jackals, known as kol-bahl, will attach themselves to a particular tiger, trailing it at a safe distance to feed on the big cat's kills.
Reproduction
Mating can occur all year round, but is more common between November and April. A female is only receptive for three to six days. Mating is frequent and noisy during that time. Gestation can range from 93 to 112 days, the average being 105 days. The litter is usually two or three cubs, occasionally as few as one or as many as six. Cubs weigh from 680 to 1400 g each at birth, and are born blind and helpless. The females rear them alone, with the birth site and maternal den in a sheltered location such as a thicket, cave or rocky crevice. The father generally takes no part in rearing them. Unrelated wandering male tigers may kill cubs to make the female receptive, since the tigress may give birth to another litter within five months if the cubs of the previous litter are lost. The mortality rate of tiger cubs is about 50% in the first two years. Few other predators attack tiger cubs due to the diligence and ferocity of the mother tiger. Apart from humans and other tigers, common causes of cub mortality are starvation, freezing, and accidents.
A dominant cub emerges in most litters, usually a male. This cub is more active than its siblings and takes the lead in their play, eventually leaving its mother and becoming independent earlier. The cubs open their eyes at six to fourteen days old. By eight weeks, the cubs make short ventures outside the den with their mother, although they do not travel with her as she roams her territory until they are older. The cubs are nursed for three to six months. Around the time they are weaned, they start to accompany their mother on territorial walks and they are taught how to hunt. The cubs often become capable (and nearly adult size) hunters at eleven months old. The cubs become independent around eighteen months of age, but it is not until they are around two to two and a half years old that they fully separate from their mother. Females reach sexual maturity at three to four years, whereas males do so at four to five years.
Conservation efforts
| Country | Estimate |
|---|---|
| Bangladesh | 440 |
| Bhutan | 75 |
| Cambodia | 20 |
| China | 45 |
| India | 2, 226 |
| Indonesia | 500 |
| Laos | 17 |
| Malaysia | 500 |
| Myanmar | 85 |
| Nepal | 155 |
| North Korea | n/a |
| Russia | 360 |
| Thailand | 200 |
| Vietnam | 20 |
| Total | 4, 968 |
The tiger is an endangered species. Poaching for fur and body parts and destruction of habitat have simultaneously greatly reduced tiger populations in the wild. At the start of the 20th century, it is estimated there were over 100, 000 tigers in the wild, but the population has dwindled outside of captivity to between 1, 500 and 3, 500. Major reasons for population decline include habitat destruction, habitat fragmentation and poaching. Demand for tiger parts for use in traditional Chinese medicine has also been cited as a major threat to tiger populations. Some estimates suggest that there are fewer than 2, 500 mature breeding individuals, with no subpopulation containing more than 250 mature breeding individuals. The global wild tiger population was estimated by the World Wide Fund for Nature at 3, 200 in 2011. The exact number of wild tigers is unknown, as many estimates are outdated or are educated guesses; few estimates are based on reliable scientific censuses. The table shows estimates per country according to IUCN and range country governments. The Wildlife Conservation Society and Panthera Corporation formed the collaboration Tigers Forever, with field sites including the world's largest tiger reserve, the 21756 km2 Hukaung Valley in Myanmar. Other reserves were in the Western Ghats, in Thailand, Laos, Cambodia, the Russian Far East and China, covering in total about 260000 km2.
India is home to the world's largest population of wild tigers but only 11% of the original Indian tiger habitat remains, and it has become fragmented and degraded. From 1973, India's Project Tiger, started by Indira Gandhi, established over 25 tiger reserves in reclaimed land, where human development was forbidden. The project was credited with tripling the number of wild Bengal tigers from some 1, 200 in 1973 to over 3, 500 in the 1990s, but a 2007 census showed that numbers had dropped back to about 1, 400 tigers because of poaching. Following the report, the Indian government pledged $153 million to the initiative, set up measures to combat poaching, promised funds to relocate up to 200, 000 villagers in order to reduce human-tiger interactions, and set up eight new tiger reserves. India also reintroduced tigers to the Sariska Tiger Reserve and by 2009 it was claimed that poaching had been effectively countered at Ranthambore National Park. A 2014 census estimated a population of 2, 226, a 30% increase since 2011.
In the 1940s, the Siberian tiger was on the brink of extinction with only about 40 animals remaining in the wild in Russia. As a result, anti-poaching controls were put in place by the Soviet Union and a network of protected zones (zapovedniks) were instituted, leading to a rise in the population to several hundred. Poaching again became a problem in the 1990s, when the economy of Russia collapsed. The major obstacle in preserving the species is the enormous territory individual tigers require (up to 450 km2 needed by a single female and more for a single male). Current conservation efforts are led by local governments and NGO's in concert with international organisations, such as the World Wide Fund for Nature and the Wildlife Conservation Society. The competitive exclusion of wolves by tigers has been used by Russian conservationists to convince hunters to tolerate the big cats. Tigers have less impact on ungulate populations than do wolves, and are effective in controlling the latter's numbers. In 2005, there were thought to be about 360 animals in Russia, though these exhibited little genetic diversity.
Having earlier rejected the Western-led environmentalist movement, China changed its stance in the 1980s and became a party to the CITES treaty. By 1993 it had banned the trade in tiger parts, and this diminished the use of tiger bones in traditional Chinese medicine.
After this, the Tibetan people's trade in tiger skins became a relatively more important threat to tigers. The pelts were used in clothing, tiger-skin chuba being worn by singers and participants in horse racing festivals, and had become status symbols. In 2004, international conservation organizations launched successful environmental propaganda campaigns in China against the Tibetan tiger skin trade. There was outrage in India, where many Tibetans live, and the 14th Dalai Lama was persuaded to take up the issue. Since then there has been a change of attitude, with some Tibetans publicly burning their chubas.
In 1994, the Indonesian Sumatran Tiger Conservation Strategy addressed the potential crisis that tigers faced in Sumatra. The Sumatran Tiger Project (STP) was initiated in June 1995 in and around the Way Kambas National Park in order to ensure the long-term viability of wild Sumatran tigers and to accumulate data on tiger life-history characteristics vital for the management of wild populations. By August 1999, the teams of the STP had evaluated 52 sites of potential tiger habitat in Lampung Province, of which only 15 these were intact enough to contain tigers. In the framework of the STP a community-based conservation programme was initiated to document the tiger-human dimension in the park in order to enable conservation authorities to resolve tiger-human conflicts based on a comprehensive database rather than anecdotes and opinions.
Rewilding
In 1978, the Indian conservationist Billy Arjan Singh attempted to rewild a tiger in Dudhwa National Park; this was the captive-bred tigress Tara. Soon after the release, numerous people were killed and eaten by a tigress that was subsequently shot. Government officials claimed it was Tara, though Singh disputed this. Further controversy broke out with the discovery that Tara was partly Siberian tiger.
The organisation Save China's Tigers has attempted to rewild the South China Tiger, with a breeding and training programme in South Africa.
Tiger as prey
The tiger has been one of the Big Five game animals of Asia. Tiger hunting took place on a large scale in the early nineteenth and twentieth centuries, being a recognised and admired sport by the British in colonial India as well as the maharajas and aristocratic class of the erstwhile princely states of pre-independence India. A single maharaja or English hunter could claim to kill over a hundred tigers in their hunting career. Tiger hunting was done by some hunters on foot; others sat up on machans with a goat or buffalo tied out as bait; yet others on elephant-back.
Man-eating tigers
Wild tigers that have had no prior contact with humans actively avoid interactions with humans. However, tigers cause more human deaths through direct attack than any other wild mammal. Attacks are occasionally provoked, as tigers lash out after being injured while they themselves are hunted. Attacks can be provoked accidentally, as when a human surprises a tiger or inadvertently comes between a mother and her young, or as in a case in rural India when a postman startled a tiger, used to seeing him on foot, by riding a bicycle. Occasionally tigers come to view people as prey. Such attacks are most common in areas where population growth, logging, and farming have put pressure on tiger habitats and reduced their wild prey. Most man-eating tigers are old, are missing teeth, and are unable to capture their preferred prey. For example, the Champawat Tiger, a tigress found in Nepal and then India, had two broken canines. She was responsible for an estimated 430 human deaths, the most attacks known to be perpetrated by a single wild animal, by the time she was shot in 1907 by Jim Corbett. According to Corbett, tiger attacks on humans are normally in daytime, when people are working outdoors and are not keeping watch. Early writings tend to describe man-eating tigers as cowardly because of their ambush tactics.
Man-eaters have been a particular problem in recent decades in India and Bangladesh, especially in Kumaon, Garhwal and the Sundarbans mangrove swamps of Bengal, where some healthy tigers have hunted humans. Because of rapid habitat loss attributed to climate change, tiger attacks have increased in the Sundarbans. The Sundarbans area had 129 human deaths from tigers from 1969 to 1971. In the 10 years prior to that period, about 100 attacks per year in the Sundarbans, with a high of around 430 in some years of the 1960s. Unusually, in some years in the Sundarbans, more humans are killed by tigers than vice versa. In 1972, India's production of honey and beeswax dropped by 50% when at least 29 people who gathered these materials were devoured. In 1986 in the Sundarbans, since tigers almost always attack from the rear, masks with human faces were worn on the back of the head, on the theory that tigers usually do not attack if seen by their prey. This decreased the number of attacks only temporarily. All other means to prevent attacks, such as providing more prey or using electrified human dummies, worked less well.
At least 27 people were killed or seriously injured by captive tigers in the United States from 1998 to 2001.
In some cases, rather than being predatory, tiger attacks on human seem to be territorial in nature. At least in one case, a tigress with cubs killed eight people entering her territory without consuming them at all.
Commercial hunting and traditional medicine
Historically, tigers have been hunted at a large scale so their famous striped skins could be collected. The trade in tiger skins peaked in the 1960s, just before international conservation efforts took effect. By 1977, a tiger skin in an English market was considered to be worth $4, 250 US dollars.
Many people in China and other parts of Asia have a belief that various tiger parts have medicinal properties, including as pain killers and aphrodisiacs. There is no scientific evidence to support these beliefs. The use of tiger parts in pharmaceutical drugs in China is already banned, and the government has made some offences in connection with tiger poaching punishable by death. Furthermore, all trade in tiger parts is illegal under the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora and a domestic trade ban has been in place in China since 1993.
However, the trading of tiger parts in Asia has become a major black market industry and governmental and conservation attempts to stop it have been ineffective to date. Almost all black marketers engaged in the trade are based in China and have either been shipped and sold within in their own country or into Taiwan, South Korea or Japan. The Chinese subspecies was almost completely decimated by killing for commerce due to both the parts and skin trades in the 1950s through the 1970s. Contributing to the illegal trade, there are a number of tiger farms in the country specialising in breeding the cats for profit. It is estimated that between 5, 000 and 10, 000 captive-bred, semi-tame animals live in these farms today. However, many tigers for traditional medicine black market are wild ones shot or snared by poachers and may be caught anywhere in the tiger's remaining range (from Siberia to India to the Malay Peninsula to Sumatra). In the Asian black market, a tiger penis can be worth the equivalent of around $300 U.S. dollars. In the years of 1990 through 1992, 27 million products with tiger derivatives were found. In July 2014 at an international convention on endangered species in Geneva, Switzerland, a Chinese representative admitted for the first time his government was aware trading in tiger skins was occurring in China.
In captivity
In Ancient Roman times, tigers were kept in menageries and amphitheatres to be exhibited, trained and paraded, and were often provoked to fight humans and exotic beasts. Since the seventeenth century, tigers, being rare and ferocious, were sought after to keep at European castles as symbols of their owners' power. Tigers became central zoo and circus exhibits in the eighteenth century: a tiger could cost up to 4, 000 francs in France (for comparison, a professor of the Beaux-Arts at Lyons earned only 3, 000 francs a year), or up to $3, 500 in the United States where a lion cost no more than $1, 000.
China (2007) had over 4, 000 captive tigers, of which 3, 000 were held by about twenty larger facilities, with the rest held by some 200 smaller facilities. The USA (2011) had 2, 884 tigers in 468 facilities. Nineteen states have banned private ownership of tigers, fifteen require a license, and sixteen states have no regulation. Genetic ancestry of 105 captive tigers from fourteen countries and regions showed that forty-nine animals belonged distinctly to five subspecies; fifty-two animals had mixed subspecies origins.
The Tiger Species Survival Plan has condemned the breeding of white tigers, alleging they are of mixed ancestry and of unknown lineage. The genes responsible for white coloration are represented by 0.001% of the population. The disproportionate growth in numbers of white tigers points to inbreeding among homozygous recessive individuals. This would lead to inbreeding depression and loss of genetic variability.
Cultural depictions
Tigers and their superlative qualities have been a source of fascination for mankind since ancient times, and they are routinely visible as important cultural and media motifs. They are also considered one of the charismatic megafauna, and are used as the face of conservation campaigns worldwide. In a 2004 online poll conducted by cable television channel Animal Planet, involving more than 50, 000 viewers from 73 countries, the tiger was voted the world's favourite animal with 21% of the vote, narrowly beating the dog.
In myth and legend
In Chinese myth and culture, the tiger is one of the 12 animals of the Chinese zodiac. In Chinese art, the tiger is depicted as an earth symbol and equal rival of the Chinese dragon – the two representing matter and spirit respectively. The Southern Chinese martial art Hung Ga is based on the movements of the tiger and the crane. In Imperial China, a tiger was the personification of war and often represented the highest army general (or present day defense secretary), while the emperor and empress were represented by a dragon and phoenix, respectively. The White Tiger () is one of the Four Symbols of the Chinese constellations. It is sometimes called the White Tiger of the West (????), and it represents the west and the autumn season.
The tiger's tail appears in stories from countries including China and Korea, it being generally inadvisable to grasp a tiger by the tail.
In Buddhism, the tiger is one of the Three Senseless Creatures, symbolising anger, with the monkey representing greed and the deer lovesickness. The Tungusic peoples considered the Siberian tiger a near-deity and often referred to it as "Grandfather" or "Old man". The Udege and Nanai called it "Amba". The Manchu considered the Siberian tiger as Hu Lin, the king. In Hinduism, the god Shiva wears and sits on tiger skin. The ten-armed warrior goddess Durga rides the tigress (or lioness) Damon into battle. In southern India the god Ayyappan was associated with a tiger.
The weretiger replaces the werewolf in shapeshifting folklore in Asia; in India they were evil sorcerers, while in Indonesia and Malaysia they were somewhat more benign.
In literature and film
In William Blake's poem in the Songs of Experience, titled "The Tyger, " the tiger is a menacing and fearful animal. In Yann Martel's 2001 Man Booker Prize winning novel Life of Pi, the protagonist, surviving shipwreck for months in a small boat, somehow avoids being eaten by the other survivor, a large Bengal tiger. The story was adapted in Ang Lee's 2012 feature film of the same name. Jim Corbett's 1944 Man-Eaters of Kumaon tells ten true stories of his tiger-hunting exploits in what is now the northern Uttarakhand region of India. The book has sold over four million copies, and has been the basis of both fictional and documentary films. In Rudyard Kipling's 1894 The Jungle Book, the tiger, Shere Khan, is the mortal enemy of the human protagonist, Mowgli; the book has formed the basis of both live-action and animated films. Other tiger characters aimed at children tend to be more benign, as for instance Tigger in A. A. Milne's Winnie-the-Pooh and Hobbes of the comic strip Calvin and Hobbes, both of whom are represented as simply stuffed animals come to life.
As a symbol
The tiger is one of the animals displayed on the Pashupati seal of the Indus Valley Civilisation. The tiger was the emblem of the Chola Dynasty and was depicted on coins, seals and banners. The seals of several Chola copper coins show the tiger, the Pandyan emblem fish and the Chera emblem bow, indicating that the Cholas had achieved political supremacy over the latter two dynasties. Gold coins found in Kavilayadavalli in the Nellore district of Andra Pradesh have motifs of the tiger, bow and some indistinct marks. The tiger symbol of Chola Empire was later adopted by the Liberation Tigers of Tamil Eelam and the tiger became a symbol of the unrecognized state of Tamil Eelam and Tamil independence movement.
The Bengal tiger is the national animal of India and Bangladesh. The Malaysian tiger is the national animal of Malaysia. The Siberian tiger is the national animal of South Korea. Since the successful economies of South Korea, Taiwan, Hong Kong and Singapore were described as the Four Asian Tigers, a tiger economy is a metaphor for a nation in rapid development. Tiger are also mascots for various sports teams around the world. Tony the Tiger is a famous mascot for Kellogg's breakfast cereal Frosted Flakes. The Esso (Exxon) brand of petrol was advertised from 1969 onwards with the slogan 'put a tiger in your tank', and a tiger mascot; more than 2.5 million synthetic tiger tails were sold to motorists, who tied them to their petrol tank caps.
This article uses material from Wikipedia released under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share-Alike Licence 3.0. Eventual photos shown in this page may or may not be from Wikipedia, please see the license details for photos in photo by-lines.
Scientific classification
- Kingdom
- Animalia
- Phylum
- Chordata
- Subphylum
- Vertebrata
- Class
- Mammalia
- Order
- Carnivora
- Family
- Felidae
- Genus
- Panthera
- Species
- Panthera tigris
Common names
- German: Tiger
- Spanish: Tigre
- French: Tigre
- Italian: Tigre
- Dutch: Tijger
- Russian: Тигр
- Swedish: Tiger
- Thai: เสือโคร่งอินโดจีน
Synonyms
- Tigris regalis, John Edward Gray (1867)
- Tigris striatus, Severtzov (1858)
- Felis tigris, Carolus Linnaeus (1758)
Conservation status

Endangered (IUCN3.1)
Photos
Please help us review our species pages if wrong photos are used or any other details in the page is wrong. We can be reached via our contact us page.
Range Map
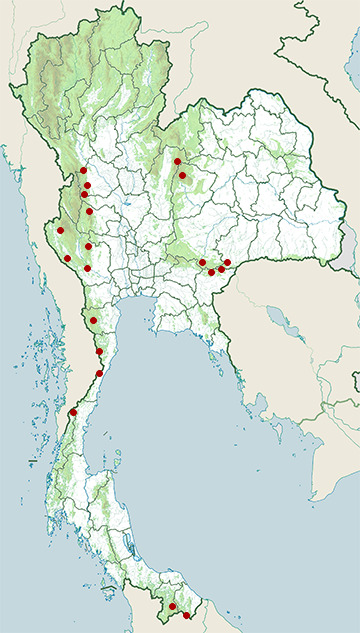
- Bang Lang National Park
- Chaloem Rattanakosin National Park
- Dong Yai Wildlife Sanctuary
- Hala-Bala Wildlife Sanctuary
- Huai Kha Khaeng Wildlife Sanctuary
- Huai Yang Waterfall National Park
- Kaeng Krachan National Park
- Khao Laem National Park
- Khlong Lan National Park
- Khlong Wang Chao National Park
- Kui Buri National Park
- Mae Wong National Park
- Nam Nao National Park
- Pang Sida National Park
- Phu Khiao Wildlife Sanctuary
- Sadeth Naikrom - Krom Luang Wildlife Sanctuary
- Sai Yok National Park
- Salak Pra Wildlife Sanctuary
- Ta Phraya National Park
- Thap Lan National Park









