Species of Thailand
Peregrine falcon
Falco peregrinus
Marmaduke Tunstall, 1771
In Thai: เหยี่ยวเพเรกริน
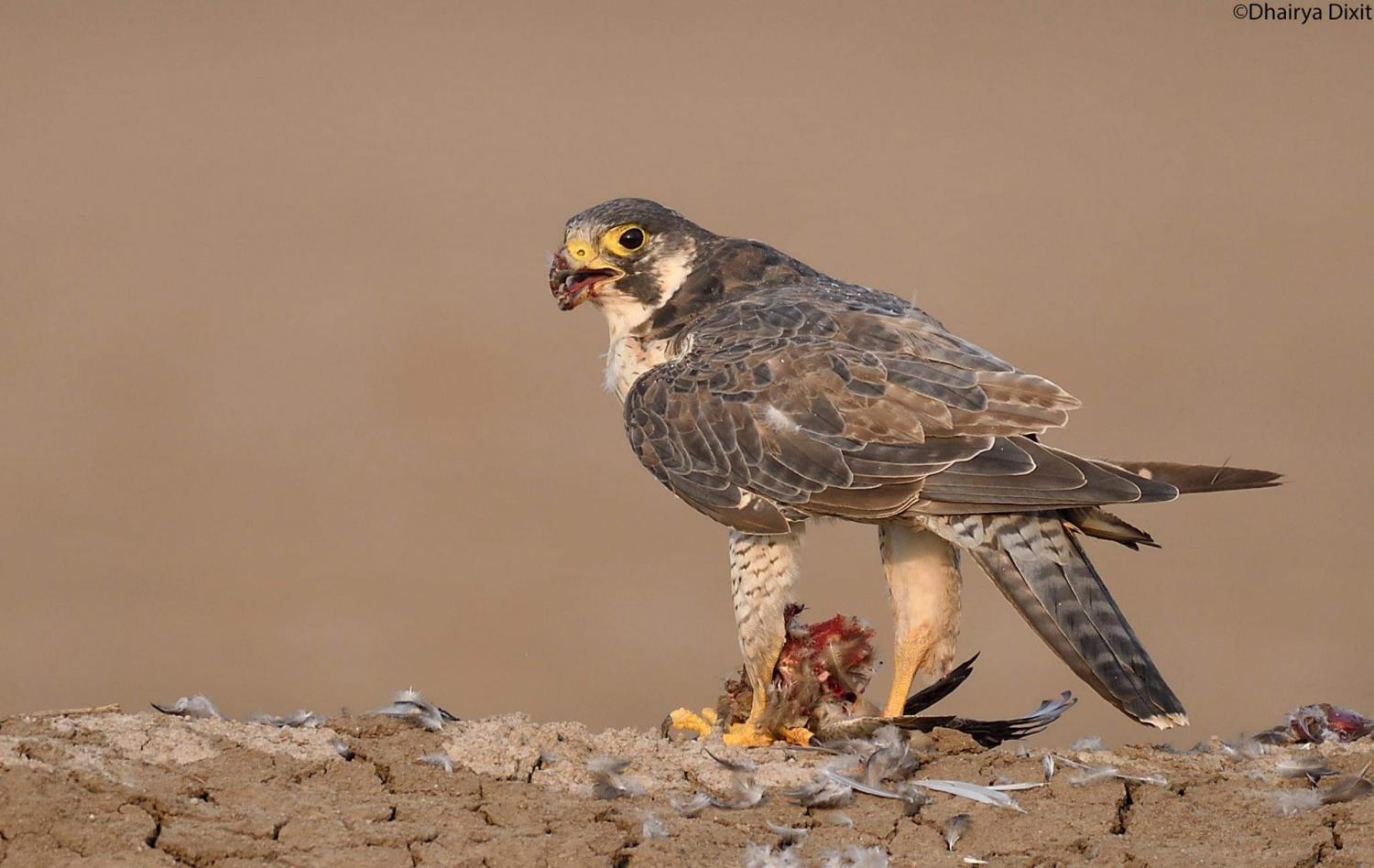
The peregrine falcon (Falco peregrinus), also known as the peregrine, and historically as the duck hawk in North America, is a widespread bird of prey (raptor) in the family Falconidae. A large, crow-sized falcon, it has a blue-grey back, barred white underparts, and a black head. The peregrine is renowned for its speed, reaching over 200 order=flip sigfig=2 during its characteristic hunting stoop (high-speed dive), making it the fastest bird in the world, as well as the fastest member of the animal kingdom. According to a National Geographic TV program, the highest measured speed of a peregrine falcon is 389 km/h. As is typical for bird-eating raptors, peregrine falcons are sexually dimorphic, with females being considerably larger than males. According to one study, it has the fastest visual processing speed of any animal tested so far, and can register discrete changes up to 129 Hz or cycles per second. Analogically, film is a series of still images projected onto a screen. Those still images need to be changing at roughly 24 frames per second before humans see them as fluid and no longer as individual, discrete pictures. The film would have to be refreshing at 129 frames per second before peregrine falcons stopped seeing flashing, still images and started seeing fluid motion.
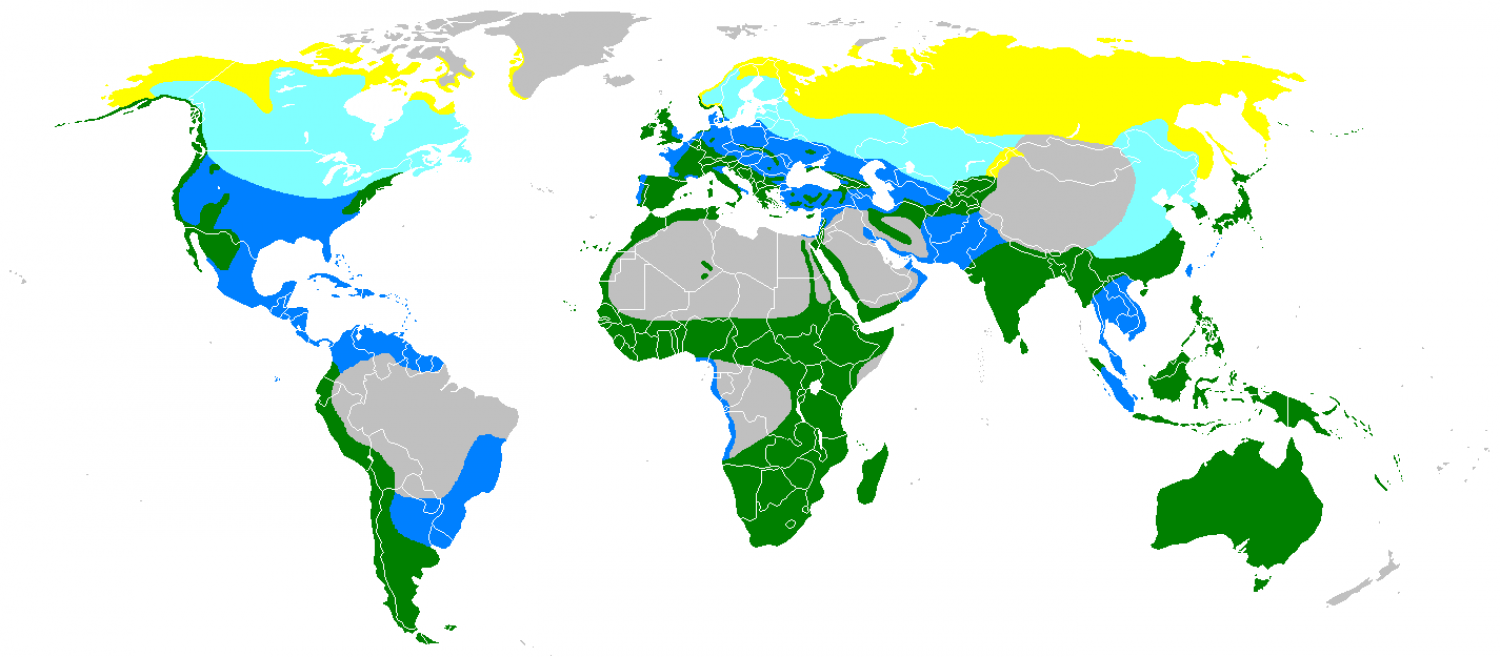
The peregrine's breeding range includes land regions from the Arctic tundra to the tropics. It can be found nearly everywhere on Earth, except extreme polar regions, very high mountains, and most tropical rainforests; the only major ice-free landmass from which it is entirely absent is New Zealand. This makes it the world's most widespread raptor, and one of the most widely found bird species. In fact, the only land-based bird species found over a larger geographic area is not always naturally occurring, but one widely introduced by humans, the rock pigeon, which in turn now supports many peregrine populations as a prey species. The peregrine is a highly successful example of urban wildlife in much of its range, taking advantage of tall buildings as nest sites and an abundance of prey such as pigeons and ducks. Both the English and scientific names of this species mean "wandering falcon, " referring to the migratory habits of many northern populations. Experts recognize 17 to 19 subspecies, which vary in appearance and range; disagreement exists over whether the distinctive Barbary falcon is represented by two subspecies of Falco peregrinus, or is a separate species, F. pelegrinoides. The two species' divergence is relatively recent, during the time of the last ice age, therefore the genetic differential between them (and also the difference in their appearance) is relatively tiny. They are only about 0.6–0.8% genetically differentiated.
Although its diet consists almost exclusively of medium-sized birds, the peregrine will occasionally hunt small mammals, small reptiles, or even insects. Reaching sexual maturity at one year, it mates for life and nests in a scrape, normally on cliff edges or, in recent times, on tall human-made structures. The peregrine falcon became an endangered species in many areas because of the widespread use of certain pesticides, especially DDT. Since the ban on DDT from the early 1970s, populations have recovered, supported by large-scale protection of nesting places and releases to the wild.
The peregrine falcon is a well-respected falconry bird due to its strong hunting ability, high trainability, versatility, and availability via captive breeding. It is effective on most game bird species, from small to large.
Description
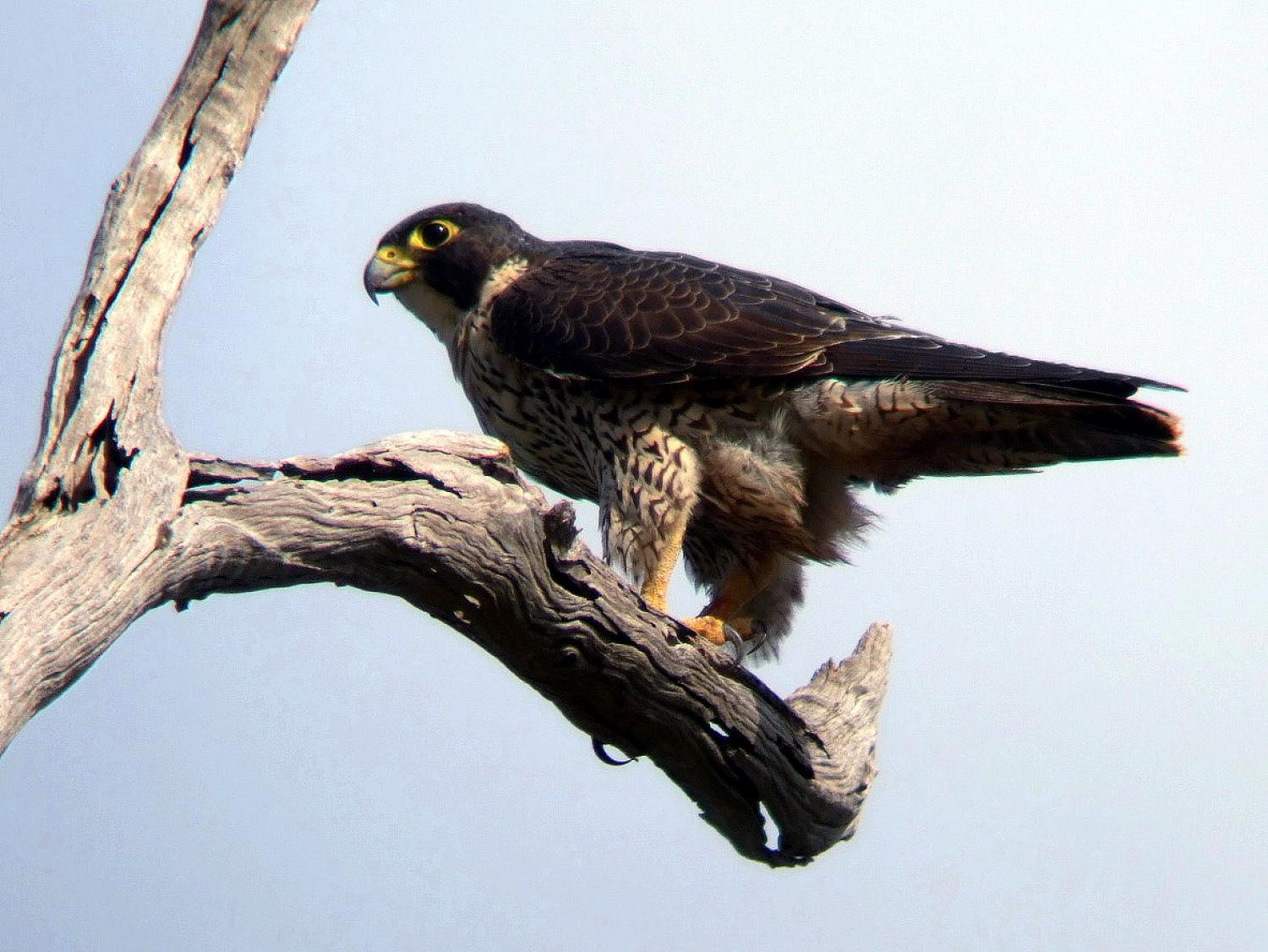
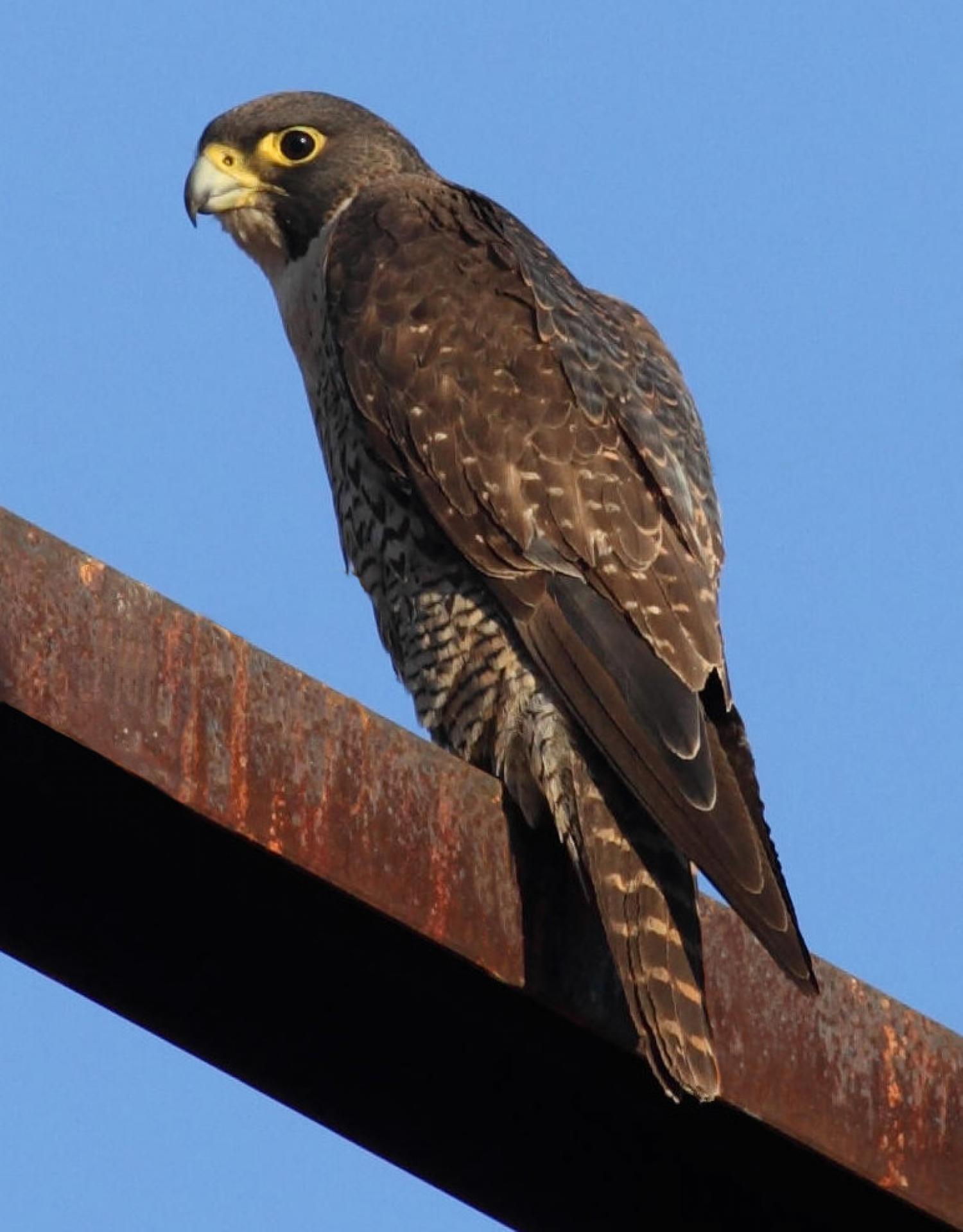
The peregrine falcon has a body length of 34 to(-) 58 cm and a wingspan from 74 to(-) 120 cm. The male and female have similar markings and plumage, but as in many birds of prey the peregrine falcon displays marked sexual dimorphism in size, with the female measuring up to 30% larger than the male. Males weigh 330 to(-) 1000 g and the noticeably larger females weigh 700 to(-) 1500 g. In most subspecies, males weigh less than 700 g and females weigh more than 800 g, with cases of females weighing about 50% more than their male breeding mates not uncommon. The standard linear measurements of peregrines are: the wing chord measures 26.5 to(-) 39 cm, the tail measures 13 to(-) 19 cm and the tarsus measures 4.5 to(-) 5.6 cm.
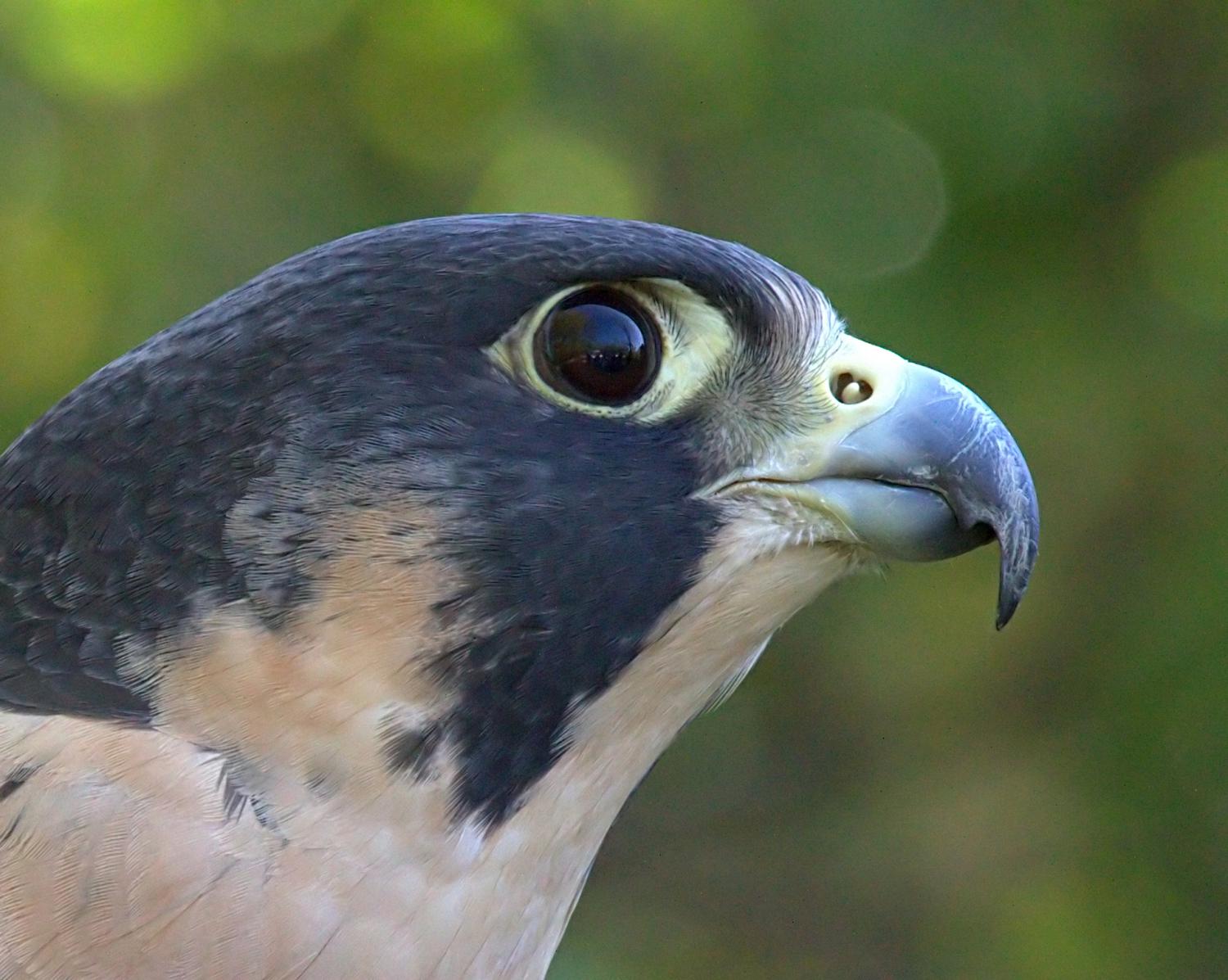
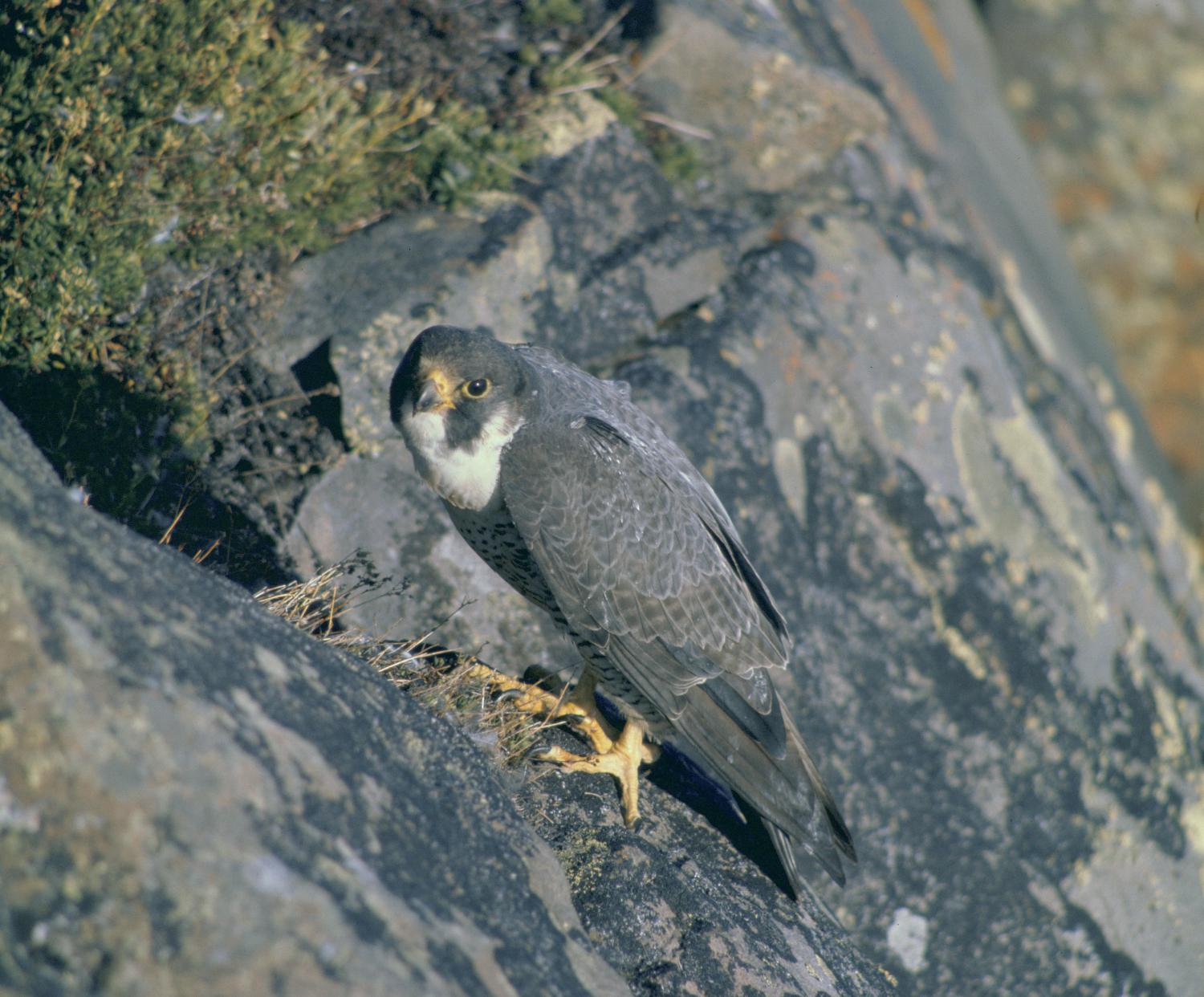
The back and the long pointed wings of the adult are usually bluish black to slate grey with indistinct darker barring (see "Subspecies" below); the wingtips are black. The white to rusty underparts are barred with thin clean bands of dark brown or black. The tail, coloured like the back but with thin clean bars, is long, narrow, and rounded at the end with a black tip and a white band at the very end. The top of the head and a "moustache" along the cheeks are black, contrasting sharply with the pale sides of the neck and white throat. The cere is yellow, as are the feet, and the beak and claws are black. The upper beak is notched near the tip, an adaptation which enables falcons to kill prey by severing the spinal column at the neck. The immature bird is much browner with streaked, rather than barred, underparts, and has a pale bluish cere and orbital ring.
Taxonomy and systematics
Falco peregrinus was first described under its current binomial name by English ornithologist Marmaduke Tunstall in his 1771 work Ornithologia Britannica. The scientific name Falco peregrinus is a Medieval Latin phrase that was used by Albertus Magnus in 1225. The specific name is taken from the fact that juvenile birds were taken while journeying to their breeding location rather than from the nest, as falcon nests were difficult to get at. The Latin term for falcon, , is related to , meaning "sickle", in reference to the silhouette of the falcon's long, pointed wings in flight.
The peregrine falcon belongs to a genus whose lineage includes the hierofalcons and the prairie falcon (F. mexicanus). This lineage probably diverged from other falcons towards the end of the Late Miocene or in the Early Pliocene, about 5–8 million years ago (mya). As the peregrine-hierofalcon group includes both Old World and North American species, it is likely that the lineage originated in western Eurasia or Africa. Its relationship to other falcons is not clear, as the issue is complicated by widespread hybridization confounding mtDNA sequence analyses. For example, a genetic lineage of the saker falcon (F. cherrug) is known which originated from a male saker producing fertile young with a female peregrine ancestor, and the descendants further breeding with sakers.
Today, peregrines are regularly paired in captivity with other species such as the lanner falcon (F. biarmicus) to produce the "perilanner", a somewhat popular bird in falconry as it combines the peregrine's hunting skill with the lanner's hardiness, or the gyrfalcon to produce large, strikingly coloured birds for the use of falconers. As can be seen, the peregrine is still genetically close to the hierofalcons, though their lineages diverged in the Late Pliocene (maybe some 2.5–2 mya in the Gelasian).
Subspecies
Numerous subspecies of Falco peregrinus have been described, with 19 accepted by the 1994 Handbook of the Birds of the World, which considers the Barbary falcon of the Canary Islands and coastal North Africa to be two subspecies (pelegrinoides and babylonicus) of Falco peregrinus, rather than a distinct species, F. pelegrinoides. The following map shows the general ranges of these 19 subspecies
- , described by Bonaparte in 1838, is known as the American peregrine falcon, or "duck hawk"; its scientific name means "duck peregrine falcon". At one time, it was partly included in leucogenys. It is mainly found in the Rocky Mountains today. It was formerly common throughout North America between the tundra and northern Mexico, where current reintroduction efforts seek to restore the population. Most mature anatum, except those that breed in more northern areas, winter in their breeding range. Most vagrants that reach western Europe seem to belong to the more northern and strongly migratory tundrius, only considered distinct since 1968. It is similar to peregrinus but is slightly smaller; adults are somewhat paler and less patterned below, but juveniles are darker and more patterned below. Males weigh 500 to(-) 700 g, while females weigh 800 to(-) 1100 g. It has become extinct in eastern North America, and populations there are hybrids as a result of reintroductions of birds from elsewhere.
- Falco peregrinus babylonicus, described by P.L. Sclater in 1861, is found in eastern Iran along the Hindu Kush and Tian Shan to Mongolian Altai ranges. A few birds winter in northern and northwestern India, mainly in dry semi-desert habitats. It is paler than pelegrinoides, and somewhat similar to a small, pale lanner falcon (Falco biarmicus). Males weigh 330 to 400 g, while females weigh 513 to 765 g.
- Falco peregrinus brookei, described by Sharpe in 1873, is also known as the Mediterranean peregrine falcon or the Maltese falcon. It includes caucasicus and most specimens of the proposed race punicus, though others may be pelegrinoides (Barbary falcons), or perhaps the rare hybrids between these two which might occur around Algeria. They occur from the Iberian Peninsula around the Mediterranean, except in arid regions, to the Caucasus. They are non-migratory. It is smaller than the nominate subspecies, and the underside usually has rusty hue. Males weigh around 445 g, while females weigh up to 920 g.
- , described by John Latham in 1790, was formerly called leucogenys and includes caeruleiceps. It breeds in the Arctic tundra of Eurasia, from Murmansk Oblast to roughly Yana and Indigirka Rivers, Siberia. It is completely migratory, and travels south in winter as far as South Asia and sub-Saharan Africa. It is often seen around wetland habitats. It is paler than peregrinus, especially on the crown. Males weigh 588 to(-) 740 g, while females weigh 925 to(-) 1333 g.
- Falco peregrinus cassini, described by Sharpe in 1873, is also known as the Austral peregrine falcon. It includes kreyenborgi, the pallid falcon, a leucistic morph occurring in southernmost South America, which was long believed to be a distinct species. Its range includes South America from Ecuador through Bolivia, northern Argentina, and Chile to Tierra del Fuego and the Falkland Islands. It is non-migratory. It is similar to nominate, but slightly smaller with a black ear region. The variation kreyenborgi is medium grey above, has little barring below, and has a head pattern like the saker falcon, but the ear region is white.
- Falco peregrinus ernesti, described by Sharpe in 1894, is found from the Sunda Islands to Philippines and south to eastern New Guinea and the nearby Bismarck Archipelago. Its geographical separation from nesiotes requires confirmation. It is non-migratory. It differs from the nominate subspecies in the very dark, dense barring on its underside and its black ear coverts.
- Falco peregrinus furuitii, described by Momiyama in 1927, is found on the Izu and Ogasawara Islands south of Honshū, Japan. It is non-migratory. It is very rare, and may only remain on a single island. It is a dark form, resembling pealei in colour, but darker, especially on the tail.
- Falco peregrinus japonensis, described by Gmelin in 1788, includes kleinschmidti, pleskei, and harterti, and seems to refer to intergrades with calidus. It is found from northeast Siberia to Kamchatka (though it is possibly replaced by pealei on the coast there) and Japan. Northern populations are migratory, while those of Japan are resident. It is similar to peregrinus, but the young are even darker than those of anatum.
- Falco peregrinus macropus, described by Swainson in 1837, is the Australian peregrine falcon. It is found in Australia in all regions except the southwest. It is non-migratory. It is similar to brookei in appearance, but is slightly smaller and the ear region is entirely black. The feet are proportionally large.
- Falco peregrinus madens, described by Ripley and Watson in 1963, is unusual in having some sexual dichromatism. If the Barbary falcon (see below) is considered a distinct species, it is sometimes placed therein. It is found in the Cape Verde Islands, and is non-migratory; it is endangered with only six to eight pairs surviving. Males have a rufous wash on crown, nape, ears, and back; underside conspicuously washed pinkish-brown. Females are tinged rich brown overall, especially on the crown and nape.
- Falco peregrinus minor, first described by Bonaparte in 1850. It was formerly often known as perconfusus. It is sparsely and patchily distributed throughout much of sub-Saharan Africa and widespread in Southern Africa. It apparently reaches north along the Atlantic coast as far as Morocco. It is non-migratory and dark coloured. This is the smallest subspecies of peregrine, with smaller males weighing as little as approximately 300 g.
- Falco peregrinus nesiotes, described by Mayr in 1941, is found in Fiji and probably also Vanuatu and New Caledonia. It is non-migratory.
- Falco peregrinus pealei, described by Ridgway in 1873, is also known as Peale's falcon, and includes rudolfi. It is found in the Pacific Northwest of North America, northwards from the Puget Sound along the British Columbia coast (including Haida Gwaii), along the Gulf of Alaska and the Aleutian Islands to the far eastern Bering Sea coast of Russia, and may also occur on the Kuril Islands and the coasts of Kamchatka. It is non-migratory. It is the largest subspecies, and it looks like an oversized and darker tundrius or like a strongly barred and large anatum. The bill is very wide. Juveniles occasionally have pale crowns. Males weigh 700 to(-) 1000 g, while females weigh 1000 to(-) 1500 g.
- Falco peregrinus pelegrinoides, first described by Temminck in 1829, is found in the Canary Islands through North Africa and the Near East to Mesopotamia. It is most similar to brookei, but is markedly paler above, with a rusty neck, and is a light buff with reduced barring below. It is smaller than the nominate subspecies; females weigh around 610 g.
- Falco peregrinus peregrinator, described by Sundevall in 1837, is known as the Indian peregrine falcon, black shaheen, Indian shaheen or shaheen falcon. It was formerly sometimes known as Falco atriceps or Falco shaheen. Its range includes South Asia from across the Indian subcontinent to Sri Lanka and Southeastern China. In India, the shaheen is reported from all states except Uttar Pradesh, mainly from rocky and hilly regions. The Shaheen is also reported from the Andaman and Nicobar Islands in the Bay of Bengal. It has a clutch size of 3 to 4 eggs, with the chicks fledging time of 48 days with an average nesting success of 1.32 chicks per nest. In India, apart from nesting on cliffs, it has also been recorded as nesting on man-made structures such as buildings and cellphone transmission towers. A population estimate of 40 breeding pairs in Sri Lanka was made in 1996. It is non-migratory, and is small and dark, with rufous underparts. In Sri Lanka this species is found to favour the higher hills while the migrant calidus is more often seen along the coast.
- , the nominate (first-named) subspecies, described by Tunstall in 1771, breeds over much of temperate Eurasia between the tundra in the north and the Pyrenees, Mediterranean region and Alpide belt in the south. It is mainly non-migratory in Europe, but migratory in Scandinavia and Asia. Males weigh 580 to(-) 750 g, while females weigh 925 to(-) 1300 g. It includes brevirostris, germanicus, rhenanus, and riphaeus.
- Falco peregrinus radama, described by Hartlaub in 1861, is found in Madagascar and the Comoros. It is non-migratory.
- Falco peregrinus submelanogenys, described by Mathews in 1912, is the Southwest Australian peregrine falcon. It is found in southwest Australia and is non-migratory.
- Falco peregrinus tundrius, described by C.M. White in 1968, was at one time included in leucogenys. It is found in the Arctic tundra of North America to Greenland, and migrates to wintering grounds in Central and South America. Most vagrants that reach western Europe belong to this subspecies, which was previously united with anatum. It is the New World equivalent to calidus. It is smaller than anatum. It is also paler than anatum; most have a conspicuous white forehead and white in ear region, but the crown and "moustache" are very dark, unlike in calidus. Juveniles are browner, and less grey, than in calidus, and paler, sometimes almost sandy, than in anatum. Males weigh 500 to(-) 700 g, while females weigh 800 to(-) 1100 g. Despite its current recognition as a valid subspecies, a population genetic study of both pre-decline (i.e., museum) and recovered contemporary populations failed to distinguish genetically the anatum and tundrius subspecies.
Barbary falcon
These birds inhabit arid regions from the Canary Islands along the rim of the Sahara through the Middle East to Central Asia and Mongolia.
Barbary falcons have a red neck patch but otherwise differ in appearance from the peregrine proper merely according to Gloger's Rule, relating pigmentation to environmental humidity. The Barbary falcon has a peculiar way of flying, beating only the outer part of its wings like fulmars sometimes do; this also occurs in the peregrine, but less often and far less pronounced. The Barbary falcon's shoulder and pelvis bones are stout by comparison with the peregrine, and its feet are smaller. Barbary falcons breed at different times of year than neighboring peregrine falcon subspecies, but they are capable of interbreeding. There is a 0.6–0.7% genetic distance in the peregrine-Barbary falcon ("peregrinoid") complex.
Ecology and behaviour
The peregrine falcon lives mostly along mountain ranges, river valleys, coastlines, and increasingly in cities. In mild-winter regions, it is usually a permanent resident, and some individuals, especially adult males, will remain on the breeding territory. Only populations that breed in Arctic climates typically migrate great distances during the northern winter.
The peregrine falcon reaches faster speeds than any other animal on the planet when performing the stoop, which involves soaring to a great height and then diving steeply at speeds of over 320 km/h sigfig=2, hitting one wing of its prey so as not to harm itself on impact. The air pressure from such a dive could possibly damage a bird's lungs, but small bony tubercles on a falcon's nostrils are theorized to guide the powerful airflow away from the nostrils, enabling the bird to breathe more easily while diving by reducing the change in air pressure. To protect their eyes, the falcons use their nictitating membranes (third eyelids) to spread tears and clear debris from their eyes while maintaining vision. A study testing the flight physics of an "ideal falcon" found a theoretical speed limit at 400 km/h for low-altitude flight and 625 km/h for high-altitude flight. In 2005, Ken Franklin recorded a falcon stooping at a top speed of 389 km/h mi/h.
The life span of peregrine falcons in the wild is up to 19 years 9 months. Mortality in the first year is 59–70%, declining to 25–32% annually in adults. Apart from such anthropogenic threats as collision with human-made objects, the peregrine may be killed by larger hawks and owls.
The peregrine falcon is host to a range of parasites and pathogens. It is a vector for Avipoxvirus, Newcastle disease virus, Falconid herpesvirus 1 (and possibly other Herpesviridae), and some mycoses and bacterial infections. Endoparasites include Plasmodium relictum (usually not causing malaria in the peregrine falcon), Strigeidae trematodes, Serratospiculum amaculata (nematode), and tapeworms. Known peregrine falcon ectoparasites are chewing lice, Ceratophyllus garei (a flea), and Hippoboscidae flies (Icosta nigra, Ornithoctona erythrocephala).
In the Arctic Peregrine falcons chasing away small rodent predators from their nesting territory and Rough-legged Hawks (Buteo lagopus) could use these hot spots as a nesting territory.
Feeding
The peregrine falcon feeds almost exclusively on medium-sized birds such as pigeons and doves, waterfowl, songbirds, and waders. This falcon tends to nest on tall buildings or bridges, and these urban dwelling birds subsist mostly on different pigeons. Worldwide, it is estimated that between 1, 500 and 2, 000 bird species (up to roughly a fifth of the world's bird species) are predated somewhere by these falcons. In North America, prey has varied in size from 3 g adj=on hummingbirds (Selasphorus and Archilochus ssp.) to a 3.1 kg adj=on sandhill crane (killed in Alaska by a peregrine in a stoop), although most prey taken by peregrines weigh from 20 g (small passerines) to 1100 g (such as ducks and gulls). The peregrine falcon takes the most diverse range of bird species of any raptor in North America, with more than 300 species having fallen victim to the falcon, including nearly 100 shorebirds. Smaller hawks and owls are regularly predated, mainly smaller falcons such as the American kestrel, merlin and sharp-shinned hawks. In urban areas, the main component of the peregrine's diet is the rock or feral pigeon, which comprise 80% or more of the dietary intake for peregrines in some cities. Other common city birds are also taken regularly, including mourning doves, common wood pigeons, common swifts, northern flickers, common starlings, American robins, common blackbirds, and corvids (such as magpies or carrion, house, and American crows). Other than bats taken at night, the peregrine rarely hunts mammals, but will on occasion take small species such as rats, voles, hares, shrews, mice and squirrels. Coastal populations of the large subspecies pealei feed almost exclusively on seabirds. In the Brazilian mangrove swamp of Cubatão, a wintering falcon of the subspecies tundrius was observed while successfully hunting a juvenile scarlet ibis. Insects and reptiles make up a small proportion of the diet, which varies greatly depending on what prey is available.
The peregrine falcon hunts most often at dawn and dusk, when prey are most active, but also nocturnally in cities, particularly during migration periods when hunting at night may become prevalent. Nocturnal migrants taken by peregrines include species as diverse as yellow-billed cuckoo, black-necked grebe, virginia rail, and common quail. The peregrine requires open space in order to hunt, and therefore often hunts over open water, marshes, valleys, fields, and tundra, searching for prey either from a high perch or from the air. Large congregations of migrants, especially species that gather in the open like shorebirds, can be quite attractive to hunting peregrines. Once prey is spotted, it begins its stoop, folding back the tail and wings, with feet tucked. Prey is typically struck and captured in mid-air; the peregrine falcon strikes its prey with a clenched foot, stunning or killing it with the impact, then turns to catch it in mid-air. If its prey is too heavy to carry, a peregrine will drop it to the ground and eat it there. If they miss the initial strike, peregrines will chase their prey in a twisting flight. Although previously thought rare, several cases of peregrines contour-hunting, i.e. using natural contours to surprise and ambush prey on the ground, have been reported and even rare cases of prey being pursued on foot. In addition, peregrines have been documented preying on chicks in nests, from birds such as kittiwakes. Prey is plucked before consumption. A recent study showed the presence of peregrines benefits non-preferred species while at the same time causing a decline in its preferred prey. As of 2018, the fastest recorded falcon was at 242 mph (nearly 390 km/h). Researchers at the University of Groningen in the Netherlands and at Oxford University used 3D computer simulations in 2018 to show that the high speed allows peregrines to gain better maneuverability and precision in strikes.
Reproduction
The peregrine falcon is sexually mature at one to three years of age, but in larger populations they breed after two to three years of age. A pair mates for life and returns to the same nesting spot annually. The courtship flight includes a mix of aerial acrobatics, precise spirals, and steep dives. The male passes prey it has caught to the female in mid-air. To make this possible, the female actually flies upside-down to receive the food from the male's talons.
During the breeding season, the peregrine falcon is territorial; nesting pairs are usually more than 1 km apart, and often much farther, even in areas with large numbers of pairs. The distance between nests ensures sufficient food supply for pairs and their chicks. Within a breeding territory, a pair may have several nesting ledges; the number used by a pair can vary from one or two up to seven in a 16-year period.
The peregrine falcon nests in a scrape, normally on cliff edges. The female chooses a nest site, where she scrapes a shallow hollow in the loose soil, sand, gravel, or dead vegetation in which to lay eggs. No nest materials are added. Cliff nests are generally located under an overhang, on ledges with vegetation. South-facing sites are favoured. In some regions, as in parts of Australia and on the west coast of northern North America, large tree hollows are used for nesting. Before the demise of most European peregrines, a large population of peregrines in central and western Europe used the disused nests of other large birds. In remote, undisturbed areas such as the Arctic, steep slopes and even low rocks and mounds may be used as nest sites. In many parts of its range, peregrines now also nest regularly on tall buildings or bridges; these human-made structures used for breeding closely resemble the natural cliff ledges that the peregrine prefers for its nesting locations.
The pair defends the chosen nest site against other peregrines, and often against ravens, herons, and gulls, and if ground-nesting, also such mammals as foxes, wolverines, felids, bears, wolves, and mountain lions. Both nests and (less frequently) adults are predated by larger-bodied raptorial birds like eagles, large owls, or gyrfalcons. The most serious predators of peregrine nests in North America and Europe are the great horned owl and the Eurasian eagle owl. When reintroductions have been attempted for peregrines, the most serious impediments were these two species of owls routinely picking off nestlings, fledglings and adults by night. Peregrines defending their nests have managed to kill raptors as large as golden eagles and bald eagles (both of which they normally avoid as potential predators) that have come too close to the nest by ambushing them in a full stoop. In one instance, when a snowy owl killed a newly fledged peregrine, the larger owl was in turn killed by a stooping peregrine parent.
The date of egg-laying varies according to locality, but is generally from February to March in the Northern Hemisphere, and from July to August in the Southern Hemisphere, although the Australian subspecies macropus may breed as late as November, and equatorial populations may nest anytime between June and December. If the eggs are lost early in the nesting season, the female usually lays another clutch, although this is extremely rare in the Arctic due to the short summer season. Generally three to four eggs, but sometimes as few as one or as many as five, are laid in the scrape. The eggs are white to buff with red or brown markings. They are incubated for 29 to 33 days, mainly by the female, with the male also helping with the incubation of the eggs during the day, but only the female incubating them at night. The average number of young found in nests is 2.5, and the average number that fledge is about 1.5, due to the occasional production of infertile eggs and various natural losses of nestlings.
After hatching, the chicks (called "es") are covered with creamy-white down and have disproportionately large feet. The male (called the "") and the female (simply called the "falcon") both leave the nest to gather prey to feed the young. The hunting territory of the parents can extend a radius of 19 to 24 km from the nest site. Chicks fledge 42 to 46 days after hatching, and remain dependent on their parents for up to two months.
Use in falconry
The peregrine falcon is a highly admired falconry bird, and has been used in falconry for more than 3, 000 years, beginning with nomads in central Asia. Its advantages in falconry include not only its athleticism and eagerness to hunt, but an equable disposition that leads to it being one of the easier falcons to train. The peregrine falcon has the additional advantage of a natural flight style of circling above the falconer ("waiting on") for game to be flushed, and then performing an effective and exciting high-speed diving stoop to take the quarry. The speed of the stoop not only allows the falcon to catch fast flying birds, it also enhances the falcon's ability to exert maneuvers to catch highly agile prey, and allows the falcon to deliver a knock out blow with a fist-like clenched talon against game that may be much larger than itself. Additionally the versatility of the species, with agility allowing capture of smaller birds and a strength and attacking style allowing capture of game much larger than themselves, combined with the wide size range of the many peregrine subspecies, means there is a subspecies suitable to almost any size and type of game bird. This size range, evolved to fit various environments and prey species, is from the larger females of the largest subspecies to the smaller males of the smallest subspecies, approximately five to one (approximately 1500 g to 300 g). The males of smaller and medium-sized subspecies, and the females of the smaller subspecies, excel in the taking of swift and agile small game birds such as dove, quail, and smaller ducks. The females of the larger subspecies are capable of taking large and powerful game birds such as the largest of duck species, pheasant, and grouse.
Peregrine falcons handled by falconers are also occasionally used to scare away birds at airports to reduce the risk of bird-plane strikes, improving air-traffic safety. They were also used to intercept homing pigeons during World War II.
Peregrine falcons have been successfully bred in captivity, both for falconry and for release back into the wild. Until 2004 nearly all peregrines used for falconry in the US were captive-bred from the progeny of falcons taken before the US Endangered Species Act was enacted and from those few infusions of wild genes available from Canada and special circumstances. Peregrine falcons were removed from the United States' endangered species list in 1999. The successful recovery program was aided by the effort and knowledge of falconers – in collaboration with The Peregrine Fund and state and federal agencies – through a technique called hacking. Finally, after years of close work with the US Fish and Wildlife Service, a limited take of wild peregrines was allowed in 2004, the first wild peregrines taken specifically for falconry in over 30 years.
The development of captive breeding methods has led to peregrines being commercially available for falconry use, thus mostly eliminating the need to capture wild birds for support of falconry. The main reason for taking wild peregrines at this point is to maintain healthy genetic diversity in the breeding lines. Hybrids of peregrines and gyrfalcons are also available that can combine the best features of both species to create what many consider to be the ultimate falconry bird for the taking of larger game such as the sage-grouse. These hybrids combine the greater size, strength, and horizontal speed of the gyrfalcon with the natural propensity to stoop and greater warm weather tolerance of the peregrine.
Decline due to pesticides
The peregrine falcon became an endangered species over much of its range because of the use of organochlorine pesticides, especially DDT, during the 1950s, '60s, and '70s. Pesticide biomagnification caused organochlorine to build up in the falcons' fat tissues, reducing the amount of calcium in their eggshells. With thinner shells, fewer falcon eggs survived until hatching. In several parts of the world, such as the eastern United States and Belgium, this species became extirpated (locally extinct) as a result. An alternate point of view is that populations in the eastern North America had vanished due to hunting and egg collection. Following the ban of organochlorine pesticides, the reproductive success of Peregrines increased in Scotland in terms of territory occupancy and breeding success, although spatial variation in recovery rates indicate that in some areas Peregrines were also impacted by other factors such as persecution.
Recovery efforts
Peregrine falcon recovery teams breed the species in captivity. The chicks are usually fed through a chute or with a hand puppet mimicking a peregrine's head, so they cannot see to imprint on the human trainers. Then, when they are old enough, the rearing box is opened, allowing the bird to train its wings. As the fledgling gets stronger, feeding is reduced, forcing the bird to learn to hunt. This procedure is called hacking back to the wild. To release a captive-bred falcon, the bird is placed in a special cage at the top of a tower or cliff ledge for some days or so, allowing it to acclimate itself to its future environment.
Worldwide recovery efforts have been remarkably successful. The widespread restriction of DDT use eventually allowed released birds to breed successfully. The peregrine falcon was removed from the U.S. Endangered Species list on 25 August 1999.
Some controversy has existed over the origins of captive breeding stock used by The Peregrine Fund in the recovery of peregrine falcons throughout the contiguous United States. Several peregrine subspecies were included in the breeding stock, including birds of Eurasian origin. Due to the extirpation of the eastern anatum (Falco peregrinus anatum), the near extirpation of the anatum in the Midwest, and the limited gene pool within North American breeding stock, the inclusion of non-native subspecies was justified to optimize the genetic diversity found within the species as a whole.
During the 1970s, peregrine falcons in Finland experienced a population bottleneck as a result of large declines associated with bio-accumulation of organochloride pesticides. However, the genetic diversity of peregrines in Finland is similar to other populations, indicating that high dispersal rates have maintained the genetic diversity of this species.
Since Peregrine eggs and chicks are still often targeted by illegal poachers, it is common practice not to publicize unprotected nest locations.
Current status
Populations of the peregrine falcon have bounced back in most parts of the world. In the United Kingdom, there has been a recovery of populations since the crash of the 1960s. This has been greatly assisted by conservation and protection work led by the Royal Society for the Protection of Birds. The RSPB has estimated that there are 1, 402 breeding pairs in the UK. In Canada, where peregrines were identified as endangered in 1978 (in the Yukon territory of northern Canada that year, only a single breeding pair was identified), the Committee on the Status of Endangered Wildlife in Canada declared the species no longer at risk in December 2017.
Peregrines now breed in many mountainous and coastal areas, especially in the west and north, and nest in some urban areas, capitalising on the urban feral pigeon populations for food. In Southampton, a nest prevented restoration of mobile telephony services for several months, after Vodafone engineers despatched to repair a faulty transmitter mast discovered a nest in the mast, and were prevented by the Wildlife and Countryside Act – on pain of a possible prison sentence – from proceeding with repairs until the chicks fledged. In many parts of the world peregrine falcons have adapted to urban habitats, nesting on cathedrals, skyscraper window ledges, tower blocks, and the towers of suspension bridges. Many of these nesting birds are encouraged, sometimes gathering media attention and often monitored by cameras.
From an ecological perspective, raptor populations in urban areas are highly beneficial. Compared with Europe, where pigeon populations have exploded to the point they are both a tourist attraction and a public nuisance. Pigeons' faeces are highly acidic, corroding historic buildings and stone statues and rusting bridge ironwork. In the United States, falcon and other raptors are in numbers high enough to ward off pigeon nest building in major highrises.
Cultural significance
Due to its striking hunting technique, the peregrine has often been associated with aggression and martial prowess. The Ancient Egyptian solar deity Ra was often represented as a man with the head of a Peregrine Falcon adorned with the solar disk. Native Americans of the Mississippian culture (c. 800–1500) used the peregrine, along with several other birds of prey, in imagery as a symbol of "aerial (celestial) power" and buried men of high status in costumes associating to the ferocity of raptorial birds. In the late Middle Ages, the Western European nobility that used peregrines for hunting, considered the bird associated with princes in formal hierarchies of birds of prey, just below the gyrfalcon associated with kings. It was considered "a royal bird, more armed by its courage than its claws". Terminology used by peregrine breeders also used the Old French term , "of noble birth; aristocratic", particularly with the peregrine.
The peregrine falcon is the national animal of the United Arab Emirates. Since 1927, the peregrine falcon has been the official mascot of Bowling Green State University in Bowling Green, Ohio. The 2007 U.S. Idaho state quarter features a peregrine falcon. The peregrine falcon has been designated the official city bird of Chicago.
The Peregrine, by J. A. Baker, is widely regarded as one of the best nature books in English written in the twentieth century. Admirers of the book include Robert Macfarlane, Mark Cocker, who regards the book as "one of the most outstanding books on nature in the twentieth century" and Werner Herzog, who called it "the one book I would ask you to read if you want to make films", and said elsewhere "it has prose of the calibre that we have not seen since Joseph Conrad". In the book, Baker recounts, in diary form, his detailed observations of peregrines (and their interaction with other birds) near his home in Chelmsford, Essex, over a single winter from October to April.
This article uses material from Wikipedia released under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share-Alike Licence 3.0. Eventual photos shown in this page may or may not be from Wikipedia, please see the license details for photos in photo by-lines.
Category / Seasonal Status
Wiki listed status (concerning Thai population): Mainly winter visitor
BCST Category: Recorded in an apparently wild state within the last 50 years
BCST Seasonal statuses:
- Resident or presumed resident
- Non-breeding visitor
Scientific classification
- Kingdom
- Animalia
- Phylum
- Chordata
- Class
- Aves
- Order
- Falconiformes
- Family
- Falconidae
- Genus
- Falco
- Species
- Falco peregrinus
Common names
- Thai: เหยี่ยวเพเรกริน
Synonyms
- Falco kreyenborgi, Otto Kleinschmidt (1929)
- Falco atriceps, Allan Octavian Hume (1929)
- Falco pelegrinoides, Coenraad Jacob Temminck (1829)
Conservation status

Least Concern (IUCN3.1)
Photos
Please help us review the bird photos if wrong ones are used. We can be reached via our contact us page.
Range Map
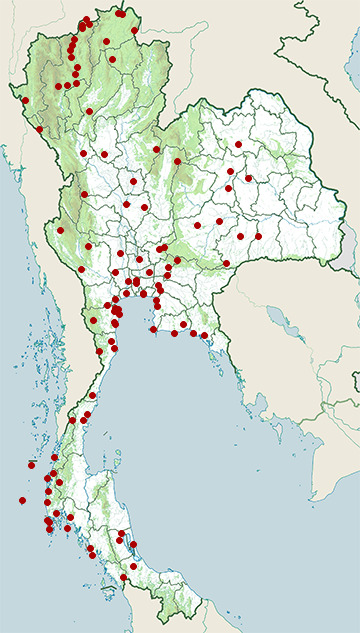
- Ao Phang-Nga National Park
- Ban Laem District, Phetchaburi
- Ban Phai District, Khon Kaen
- Ban Pho District, Chachoengsao
- Ban Sang District, Prachinburi
- Bang Phra Non-Hunting Area
- Bang Pu Recreation Centre
- Bang Saphan Noi District, Prachuap Khiri Khan
- Bangkok Province
- Bueng Boraped Non-Hunting Area
- Cha-Am District, Phetchaburi
- Chaloem Rattanakosin National Park
- Chiang Dao District, Chiang Mai
- Chiang Dao Wildlife Sanctuary
- Chiang Saen District, Chiang Rai
- Doi Inthanon National Park
- Doi Lang
- Doi Lo District, Chiang Mai
- Doi Pha Hom Pok National Park
- Fang District, Chiang Mai
- Hat Chao Mai National Park
- Hat Yai District, Songkhla
- Huai Chorakhe Mak Reservoir Non-Hunting Area
- Kaeng Khoi District, Saraburi
- Kaeng Krachan National Park
- Kamphaeng Saen District, Nakhon Pathom
- Kantharawichai District, Maha Sarakham
- Khao Dinsor (Chumphon Raptor Center)
- Khao Laem National Park
- Khao Laem Ya - Mu Ko Samet National Park
- Khao Nang Phanthurat Forest Park
- Khao Sam Roi Yot National Park
- Khao Sok National Park
- Khao Yai National Park
- Khao Yoi District, Phetchaburi
- Khung Kraben Non-Hunting Area
- Khura Buri District, Phang Nga
- Klaeng District, Rayong
- Ko Libong
- Ko Phra Thong
- Kui Buri National Park
- Kumphawapi District, Udon Thani
- Laem Pak Bia
- Laem Son National Park
- Mae Ai District, Chiang Mai
- Mae Moei National Park
- Mae Taeng District, Chiang Mai
- Mae Wong National Park
- Muak Lek District, Saraburi
- Mueang Chachoengsao District, Chachoengsao
- Mueang Chiang Mai District, Chiang Mai
- Mueang Chonburi District, Chonburi
- Mueang Chumphon District, Chumphon
- Mueang Khon Kaen District, Khon Kaen
- Mueang Krabi District, Krabi
- Mueang Lamphun District, Lamphun
- Mueang Nonthaburi District, Nonthaburi
- Mueang Phatthalung District, Phatthalung
- Mueang Phayao District, Phayao
- Mueang Phetchaburi District, Phetchaburi
- Mueang Phuket District, Phuket
- Mueang Samut Sakhon District, Samut Sakhon
- Mueang Samut Songkhram District, Samut Songkhram
- Mueang Suphanburi District, Suphan Buri
- Mueang Surin District, Surin
- Mueang Tak District, Tak
- Nam Nao National Park
- Namtok Phlio National Park
- Non Din Daeng District, Buriram
- Non Thai District, Nakhon Ratchasima
- Nong Bong Khai Non-Hunting Area
- Pak Phli District, Nakhon Nayok
- Pak Thale
- Pha Daeng National Park
- Phaisali District, Nakhon Sawan
- Phan District, Chiang Rai
- Phi Phi Islands
- Phimai District, Nakhon Ratchasima
- Phra Nakhon Si Ayutthaya District, Phra Nakhon Si Ayutthaya
- Phu Chi Fa Forest Park
- Phu Hin Rong Kla National Park
- Phutthamonthon District, Nakhon Pathom
- Pran Buri District, Prachuap Khiri Khan
- Ramkhamhaeng National Park
- Sai Yok District, Kanchanaburi
- Salawin National Park
- Samut Prakan Province
- San Sai District, Chiang Mai
- Sathing Phra District, Songkhla
- Sattahip District, Chonburi
- Similan Islands
- Sirinat National Park
- Sop Prap District, Lampang
- Surin Islands
- Takua Pa District, Phang Nga
- Taphan Hin District, Phichit
- Thai Mueang District, Phang Nga
- Thalang District, Phuket
- Thale Ban National Park
- Thale Noi Non-Hunting Area
- Thanyaburi District, Pathum Thani
- Wang Mai Forest Restoration Project